A comparative study between Embosphere(®) and conventional transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for treatment of unresectable liver metastasis from GIST
- PMID: 24653635
- PMCID: PMC3937743
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2014.02.11
A comparative study between Embosphere(®) and conventional transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for treatment of unresectable liver metastasis from GIST
Abstract
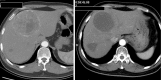
Objective: Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) is a standard treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and/or some unresectable liver metastasis tumors. Hypervascular liver metastatic lesions such as metastasis from gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) are an indication for transcatheter arterial embolization (TAE). The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Embosphere(®)-TAE (Embo-TAE) in comparison with conventional TACE (cTACE) for the treatment of liver metastasis from GIST.
Methods: A total of 45 patients who underwent TACE between Aug 2008 and Feb 2013 were enrolled. Patients with GIST who underwent TAE with Embosphere(®) (n=19) were compared with controls who received cTACE (n=26). The primary end points were treatment response and treatment-related adverse events. The secondary end points were progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS).
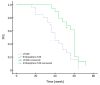
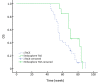
Results: The treatment response of Embo-TAE group was significantly higher than that of the cTACE group (P<0.001). The PFS was significantly better in the Embosphere(®)-group than in the cTACE group (56.6 and 42.1 weeks, respectively; P=0.003). However, there was no statistically significant difference in liver toxicity between the two groups (P>0.05). The median OS in the Embo-TAE group was longer than that in the cTACE group (74.0 weeks, 95% CI: 68.2-79.8 vs. 61.7 weeks, 95% CI: 56.2-67.2 weeks) (unadjusted P=0.045). The use of Embo-TAE significantly reduced the risk of death in patients with GIST with liver metastases according to the Cox proportional hazards regression model [hazard ratio (HR): 0.149; 95% CI: 0.064-0.475].
Conclusions: TAE with Embosphere(®) showed better treatment response and delayed tumor progression compared with cTACE. There was no significant difference in treatment-related hepatic toxicities. Embo-TAE thus appears to be a feasible and promising approach in the treatment of liver metastasis from GIST.
Keywords: Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE); embolization; gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST).
Figures

References
-
- Joensuu H, Fletcher C, Dimitrijevic S, et al. Management of malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Lancet Oncol 2002;3:655-64 - PubMed
-
- Goettsch WG, Bos SD, Breekveldt-Postma N, et al. Incidence of gastrointestinal stromal tumours is underestimated: results of a nation-wide study. Eur J Cancer 2005;41:2868-72 - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi K, Gupta S, Trent JC, et al. Hepatic artery chemoembolization for 110 gastrointestinal stromal tumors: response, survival, and prognostic factors. Cancer 2006;107:2833-41 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
