Pilonidal sinus: a comparative study of treatment methods
- PMID: 24653753
- PMCID: PMC3956091
Pilonidal sinus: a comparative study of treatment methods
Abstract
Introduction: Pilonidal disease is a very common anorectal problem without a clinical consensus on its optimal management.
Objective: To compare the methods used by our clinic and determine the outcomes in relation to healing, hospitalization time and recurrence.
Materials and methods: We have studied all the cases of patients with pilonidal sinus that were treated surgically in our clinic from January 1, 1997 to December 31, 1999.
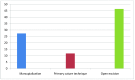
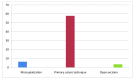
Results: A total of 111 patients were treated of whom 92 (82,8%) were men and 19 (17,2%) were women. Ages ranged from 16 to 65 years with an average age of about 25,1 years. Of the 111 patients, 63 were treated with marsupializationand the remaining 48 were treated by excision (29 with open excision and 19 with the primary suture technique). One hundred and two (91,9%) patients were discharged from the hospital after the surgical procedure, while the remaining 9 patients were hospitalized for 24 hours. The healing time for marsupialization was 27,3 days, the primary suture technique was 11,7 days and the open excision method took 46,4 days. Recurrence was observed in 16 patients (14,4%). Recurrence appeared in 4 (6,35%) of the 63 patients subjected to marsupialization, 1 of the 29 patients subjected to open incision, and 11 (57,8%) of the 19 patients subjected to primary closure.
Conclusion: In the absence of inflammation and/or recurrence, marsupialization is the surgical method of choice as it has a low percentage of recurrence and an acceptably short healing period.In apparently large, inflamed and recurrent situations, open excision is preferred.
Keywords: healing time; marsupialization; open excision; primary closure; recurrence.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparative analysis of four different surgical methods for treatment of sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus.Asian J Surg. 2019 Oct;42(10):907-913. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2018.12.011. Epub 2019 Jan 23. Asian J Surg. 2019. PMID: 30685149
-
How to repair the surgical defect after excision of sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus: a dilemma.J Wound Care. 2014 Dec;23(12):630-3. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2014.23.12.630. J Wound Care. 2014. PMID: 25492279 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of three methods in surgical treatment of pilonidal disease.ANZ J Surg. 2001 Jun;71(6):362-4. ANZ J Surg. 2001. PMID: 11409022 Review.
-
A pediatric surgeon's 35-year experience with pilonidal disease in a Canadian children's hospital.Can J Surg. 2011 Feb;54(1):39-42. doi: 10.1503/cjs.028509. Can J Surg. 2011. PMID: 21251431 Free PMC article.
-
Pilonidal sinus disease.J Visc Surg. 2013 Sep;150(4):237-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jviscsurg.2013.05.006. Epub 2013 Aug 1. J Visc Surg. 2013. PMID: 23911903 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of postoperative quality of life of Limberg flap and Karydakis flap in pilonidal sinus operations.Turk J Surg. 2020 Mar 18;36(1):59-64. doi: 10.5578/turkjsurg.4598. eCollection 2020 Mar. Turk J Surg. 2020. PMID: 32637877 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of RD2 Ver.02, a whole blood clot therapy, coupled with a minimally invasive procedure in pilonidal sinus: a phase II study.Tech Coloproctol. 2024 Aug 13;28(1):97. doi: 10.1007/s10151-024-02973-9. Tech Coloproctol. 2024. PMID: 39136828 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of Limberg and Karydakis flap in recurrent pilonidal sinus disease.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2015 May;70(5):350-5. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2015(05)08. Epub 2015 May 1. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2015. PMID: 26039952 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative Outcomes of Surgical Techniques for Pilonidal Sinus: A Turkish Retrospective Study.Med Sci Monit. 2025 Feb 25;31:e947466. doi: 10.12659/MSM.947466. Med Sci Monit. 2025. PMID: 39995244 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the coexistence of pilonidal sinus disease and hirsutism in female patients: a retrospective cross-sectional study.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 Feb 17;85(2):130-135. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000000116. eCollection 2023 Feb. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023. PMID: 36845798 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sondenaa K, Andersen E, Nesvik I. Patient characteristics and symptoms in chronic pilonidal sinus disease. Int J Colorectal Dis. . 1995;10:39–42. - PubMed
-
- Akinci OF, Bozer M, Uzunkoy A. Incidence and aetiological factors in pilonidal sinus among Turkish soldiers. Eur J Surg. 1999;165:339–342. - PubMed
-
- Louis A Buie. Classic articles in colonic and rectal surgery. 1890-1975: Jeep disease (pilonidal disease of mechanized warfare). Dis Colon Rectum. 1982;25:384–390. - PubMed
-
- King ES. The nature of the pilonidal sinus. Aust N Z J Surg. 1947;16:182–192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical