Phenotypic spectrum and hormonal profile in hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
- PMID: 24653756
- PMCID: PMC3956095
Phenotypic spectrum and hormonal profile in hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
Abstract
Background: Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (HH) is characterized by inappropriately low serum concentration of LH (luteinizing hormone) and FSH (follicle-stimulated hormone) in the setting of hypogonadism. A number of pathologic processes cause Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism but it can also occur as a part of various congenital syndromes. Objectives. To characterize the morphotypes and the hormonal profile of the HH patients enrolled in the COST Action BM1105 within "C.I. Parhon" National Institute of Endocrinology from May 2012 onward. Methods. The eligible patients were selected by using a general protocol that included: a detailed familial and personal history; a clinical evaluation focusing on genital development; a hormonal evaluation that aimed to exclude the acquired causes of HH and to characterize the basal/stimulated (triptoreline) profile of gonadotropins; a DNA extraction for genetic studies.
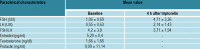
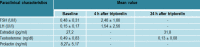
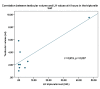
Results: We examinated the medical records of patients admitted in our institute with the diagnosis of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism from May 2012 onward. There were 19 patients: 12 males and 7 females, age at diagnosis 28.03 ± 11.45 years (13.4-56 years). The phenotypic expressions were variable and the hormonal evaluation showed low values of basal and stimulated gonadotropins.
Conclusions: Although hypogonadotropic hypogonadism is a rare disease, the monospeciality profile of National Institute of Endocrinology enable the enrolment of a high number of patients in order to create clinical guidelines for evaluation/diagnosis and for treating GnRH deficient patients.
Keywords: Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism; hormonal profile; morphotypes.
Figures





References
-
- Crowley W Jr, Filicori M, Spratt DI. The physiology of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) secretion in men and women. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1985;41:473–531. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman AR, Crowley WF. Introduction of puberty in men by long-term pulsatile administration of low-dose gonadotropin-releasing hormone. N Engl J Med. 1982;307:1237–1241. - PubMed
-
- Grumbach MM. A window of opportunity: the diagnosisof gonadotropin deficiency in the mail infant. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:3122–3127. - PubMed
-
- Nachtigall LB, Boepple PA, Pralong FP. dult-onset idiophatic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism a treateble form of male infertility. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:410–415. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
