Ankylosing spondylitis functional and activity indices in clinical practice
- PMID: 24653763
- PMCID: PMC3956102
Ankylosing spondylitis functional and activity indices in clinical practice
Abstract
Background: Clinicians have at hand several indices to evaluate disease activity and functionality in ankylosing spondylitis (AS), in order to evaluate the prognostic and the treatment of AS patients.
Objectives: to examine the relationship between functional and activity scores in AS; to note whether disease activity is associated with any clinical or laboratory variables.
Methods: the study included AS patients, classified according to the revised New York criteria; data recorded: demographics, disease duration, type of articular involvement, HLA B27 presence, history of uveitis, calculation of BASFI, BASDAI and ASDASCRP, quantification of inflammation markers.
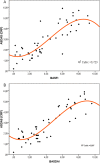
Results: 50 AS patients; ASDASCRP correlated significantly (p < 0.001) with BASFI (r = 811), BASDAI (r = 0.810) and with erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR; r = 0.505); HLA B27 positive patients had a median BASDAI 5 times higher than HLA B27 negative patients (p = 0.033); compared with patients with strictly axial disease form, patients with axial and peripheral disease had a median ESR 3 times higher (p = 0.042) and a median BASDAI 2 times higher (p = 0.050).
Conclusions: functional and activity AS indices are strongly correlated in assessing disease severity; inflammation and HLA B27 can predict the high value of these indices; axial and peripheral disease pattern is associated with higher disease activity.
Keywords: ASDAS; BASDAI; BASFI; ankylosing spondylitis.
Figures





References
-
- Dougados M, van der LS. The European Spondylarthropathy Study Group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1991;34:1218–1227. - PubMed
-
- Ward MM. Functional disability predicts total costs in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:223–231. - PubMed
-
- Calin A, Garrett S. A new approach to defining functional ability in ankylosing spondylitis: the development of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index. J Rheumatol. 1994;21:2281–2285. - PubMed
-
- Garrett S, Jenkinson T. A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity . Index. J Rheumatol. 1994;21:2286–2291. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
