Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with restless legs syndrome in spine clinic
- PMID: 24653801
- PMCID: PMC3958578
- DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2014.55.2.83
Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with restless legs syndrome in spine clinic
Abstract
Objective: The restless legs syndrome (RLS) is a common disorder affecting up to 5% to 15% of the general population, in which the incidence increases with age, and includes paresthesia in the legs. The purpose of this study is to investigate the incidence of RLS in spine center and to review clinical manifestations of this syndrome and its current treatments.
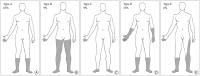
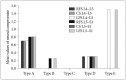
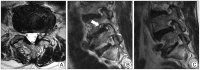
Methods: Over a period of a year, retrospective medical record review and lumbar magnetic resonance images were performed on 32 patients with RLS in spine clinic who were diagnosed by National Institutes of Health criteria. Affected limbs were classified as five. Two grading systems were used in the evaluation of neural compromises.
Results: The incidence of RLS was 5.00% (32/639). There were 16 males (50%) and 16 females (50%). The median age at diagnosis was 55.4 years (range, 25-93 years). There are no correlation between the affected limbs of RLS and neural compromises on the lumbar spine.
Conclusion: The RLS is a clearly common neurologic disorder of the limbs, usually the legs. The awareness of this syndrome can help reduce diagnostic error; thereby, avoiding the morbidity and expense associated with unnecessary studies or inappropriate treatments in RLS patients.
Keywords: Insomnia; Lumbar disc herniation; Pramipexole; Pregabalin; Restless legs syndrome; Spinal stenosis.
Figures
References
-
- Allen R. Dopamine and iron in the pathophysiology of restless legs syndrome (RLS) Sleep Med. 2004;5:385–391. - PubMed
-
- Allen R, Chen C, Soaita A, Wohlberg C, Knapp L, Peterson BT, et al. A randomized, double-blind, 6-week, dose-ranging study of pregabalin in patients with restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2010;11:512–519. - PubMed
-
- Allen RP, Barker PB, Wehrl F, Song HK, Earley CJ. MRI measurement of brain iron in patients with restless legs syndrome. Neurology. 2001;56:263–265. - PubMed
-
- Allen RP, Earley CJ. Augmentation of the restless legs syndrome with carbidopa/levodopa. Sleep. 1996;19:205–213. - PubMed
-
- Allen RP, Earley CJ. Restless legs syndrome : a review of clinical and pathophysiologic features. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2001;18:128–147. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

