Nasal Colonization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Patients with Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media
- PMID: 24653875
- PMCID: PMC3936563
- DOI: 10.7874/kja.2012.16.2.75
Nasal Colonization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Patients with Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media
Abstract
Background and objectives: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is one of major pathogens in patients with chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM). In addition to intrinsic MRSA infection of the mastoid air cell system, nasal colonization of MRSA, a known predictor of postoperative surgical site infection, may pose increased risk of postoperative complications. The purpose of this study is to describe microbiology of preoperative nasal swab screening and localized middle ear specimens in patients undergoing otologic surgeries.
Subjects and methods: Forty-nine consecutive patients with CSOM who underwent middle ear surgery were included. Preoperative nasal swabs for MRSA, and preoperative and intraoperative middle ear swabs were collected and compared for pathogens.
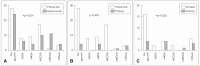
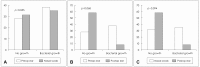
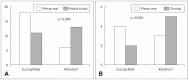
Results: Preoperative nasal swab screening confirmed MRSA colonization in 3/49 patients (6.1%) and methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative Staphylococcus (MRCNS) in 9/49 patients (18.4%). Correlation with preoperative culture results and nasal swab screening results were compatible in 2/4 patients with positive nasal swab for MRSA and 1/9 patients with positive nasal swab for MRCNS. Postoperative conversion to MRSA was observed in 3 patients.
Conclusions: The rate of nasal MRSA colonization among patients with CSOM was higher than among the general community. Preoperative MRSA colonization was associated with MRSA from middle ear specimens. Further studies are warranted to investigate the possible benefit of preoperative treatment of MRSA colonized patients undergoing middle ear surgeries.
Keywords: Culture; Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; Otitis media.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative results of bacterial culture from patients with chronic suppurative otitis media.Otol Neurotol. 2012 Jan;33(1):54-9. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e31823dbc70. Otol Neurotol. 2012. PMID: 22143302
-
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Nasal Swab Is Insufficient to Withhold Empiric Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Pneumonia Coverage in a Trauma Population.J Surg Res. 2023 May;285:45-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2022.12.014. Epub 2023 Jan 12. J Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 36640609
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization in otitis-prone children.Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011 Dec;137(12):1217-22. doi: 10.1001/archoto.2011.192. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011. PMID: 22183900
-
Systematic Review of the Clinical Utility of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Nasal Screening for MRSA Pneumonia.Ann Pharmacother. 2019 Jun;53(6):627-638. doi: 10.1177/1060028018823027. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Ann Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30600697
-
Nasal colonization of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2019 Sep 5;18(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12941-019-0324-y. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2019. PMID: 31488199 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Biofilm formation on tympanostomy tubes depends on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus genetic lineage.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Mar;273(3):615-20. doi: 10.1007/s00405-015-3607-8. Epub 2015 Mar 22. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 25796207
References
-
- Bluestone CD. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of chronic suppurative otitis media: implications for prevention and treatment. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1998;42:207–223. - PubMed
-
- Lee SK, Yeo SG, Hong SM, Sim JS, Hong CK, Lee YC, et al. Bacteriology of chronic otitis media: changing of detection rate of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2008;51:9–15.
-
- Shim HJ, Park CH, Kim MG, Lee SK, Yeo SG. A pre- and postoperative bacteriological study of chronic suppurative otitis media. Infection. 2010;38:447–452. - PubMed
-
- Yu YI, Cha CI, Lee IY, Byun JY, Cho JS. Current bacteriology of chronic suppurative otitis media. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2004;47:607–611.
-
- Ahn JH, Kim MN, Suk YA, Moon BJ. Preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative results of bacterial culture from patients with chronic suppurative otitis media. Otol Neurotol. 2012;33:54–59. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

