Development of animal models of otitis media
- PMID: 24653896
- PMCID: PMC3936519
- DOI: 10.7874/kja.2013.17.1.9
Development of animal models of otitis media
Abstract
Otitis media is defined as inflammation of the middle ear, including the auditory ossicles and the Eustachian tube. Otitis media is a major health problem in many societies. The causes of otitis media includes infection and anatomic/physiologic, host, and environmental factors. In general, otitis media is a childhood disease, and anatomic and physiologic changes have great effects on its development. Thus, in vitro or human experimental studies of otitis media are difficult. Several experimental animal models have been introduced to investigate the pathogenesis and treatment of otitis media. However, none are ideal. The aim of this review is to provide a brief overview of the current status of animal models of otitis media with effusion, acute otitis media, and cholesteatoma. This review will assist determination of the most appropriate animal models of otitis media.
Keywords: Animal model; Cholesteatoma; In vitro; Otitis media.
Figures

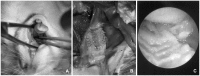
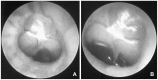
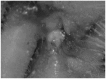
Similar articles
-
Otitis media and eustachian tube dysfunction: connection to allergic rhinitis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997 Feb;99(2):S787-97. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(97)70130-1. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9042072 Review.
-
The evaluation of the angles of Eustachian tubes in the patients with chronic otitis media on the temporal computerized tomography.Niger J Clin Pract. 2016 May-Jun;19(3):318-22. doi: 10.4103/1119-3077.179274. Niger J Clin Pract. 2016. PMID: 27022791
-
A 3-D analysis of the protympanum in human temporal bones with chronic ear disease.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;274(3):1357-1364. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-4396-4. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 27878362 Free PMC article.
-
[Changes in the middle ear mucosa of the Wistar rat after experimental resection and obstruction of the eustachian tube].Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. 1998 Jan-Feb;49(1):9-13. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. 1998. PMID: 9557301 Spanish.
-
[Seromucous otitis].Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac. 2007 Jul;124(3):120-5. doi: 10.1016/j.aorl.2006.10.007. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac. 2007. PMID: 17434139 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Development of an In Vivo Model for Eustachian Tube Dysfunction.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Jul 15;9(7):317. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9070317. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35877368 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-inflammatory interleukins in middle ear effusions from atopic and non-atopic children with chronic otitis media with effusion.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Jun;273(6):1369-78. doi: 10.1007/s00405-015-3683-9. Epub 2015 Jun 16. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 26078091
-
Surfactant Protein A Can Affect Macrophage Phagocytosis: An Important Pathogenic Mechanism of Otitis Media with Effusion.J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2023 Apr;24(2):171-180. doi: 10.1007/s10162-023-00893-3. Epub 2023 Feb 23. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 36820988 Free PMC article.
-
Stenting the Eustachian tube to treat chronic otitis media - a feasibility study in sheep.Head Face Med. 2018 May 4;14(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13005-018-0165-5. Head Face Med. 2018. PMID: 29728102 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Otitis media susceptibility due to genetic variants.Front Genet. 2023 Dec 12;14:1341669. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1341669. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 38152651 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Rovers MM. The burden of otitis media. Vaccine. 2008;26(Suppl 7):G2–G4. - PubMed
-
- Teele DW, Klein JO, Rosner B. Epidemiology of otitis media during the first seven years of life in children in greater Boston: a prospective, cohort study. J Infect Dis. 1989;160:83–94. - PubMed
-
- Casselbrant ML, Mandel EM. Acute Otitis Media and Otitis Media with Effusion. In: Flint PW, Haughey BH, Lund VJ, Niparko JK, Richardson MA, Robbins KT, editors. Cummings Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Mosby; 2010. pp. 2761–2777.
-
- Capra AM, Lieu TA, Black SB, Shinefield HR, Martin KE, Klein JO. Costs of otitis media in a managed care population. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2000;19:354–355. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

