Multifunctional Fe₃O₄@polydopamine core-shell nanocomposites for intracellular mRNA detection and imaging-guided photothermal therapy
- PMID: 24654734
- PMCID: PMC4564054
- DOI: 10.1021/nn500722y
Multifunctional Fe₃O₄@polydopamine core-shell nanocomposites for intracellular mRNA detection and imaging-guided photothermal therapy
Abstract
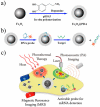
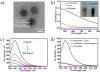
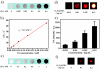
Multifunctional nanocomposites have the potential to integrate sensing, diagnostic, and therapeutic functions into a single nanostructure. Herein, we synthesize Fe3O4@polydopamine core-shell nanocomposites (Fe3O4@PDA NCs) through an in situ self-polymerization method. Dopamine, a melanin-like mimic of mussel adhesive proteins, can self-polymerize to form surface-adherent polydopamine (PDA) films onto a wide range of materials including Fe3O4 nanoparticles used here. In such nanocomposites, PDA provides a number of advantages, such as near-infrared absorption, high fluorescence quenching efficiency, and a surface for further functionalization with biomolecules. We demonstrate the ability of the Fe3O4@PDA NCs to act as theranostic agents for intracellular mRNA detection and multimodal imaging-guided photothermal therapy. This work would stimulate interest in the use of PDA as a useful material to construct multifunctional nanocomposites for biomedical applications.
Figures


References
-
- Lee JE, Lee N, Kim T, Kim J, Hyeon T. Multifunctional Mesoporous Silica Nanocomposite Nanoparticles for Theranostic Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011;44:893–902. - PubMed
-
- Lee D-E, Koo H, Sun I-C, Ryu JH, Kim K, Kwon IC. Multifunctional Nanoparticles for Multimodal Imaging and Theragnosis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012;41:2656–2672. - PubMed
-
- Gao J, Gu H, Xu B. Multifunctional Magnetic Nanoparticles: Design, Synthesis, and Biomedical Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009;42:1097–1107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

