Canine T-zone lymphoma: unique immunophenotypic features, outcome, and population characteristics
- PMID: 24655022
- PMCID: PMC4895451
- DOI: 10.1111/jvim.12343
Canine T-zone lymphoma: unique immunophenotypic features, outcome, and population characteristics
Abstract
Background: Canine T-cell lymphoma (TCL) is clinically and histologically heterogeneous with some forms, such as T-zone lymphoma (TZL), having an indolent course. Immunophenotyping is an important tool in the classification of TCL in people, and can be equally useful in dogs.
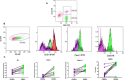
Hypothesis/objectives: We hypothesized that loss of expression of the CD45 antigen is a specific diagnostic feature of TZL.
Animals: Twenty dogs with concurrent histology and immunophenotyping by flow cytometry were studied in depth. An additional 494 dogs diagnosed by immunophenotyping were used to characterize the population of dogs with this disease.
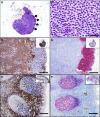
Methods: Lymph node biopsies from 35 dogs with TCL were classified by 2 pathologists using WHO criteria. Twenty lymph nodes were from dogs with CD45- TCL and 15 were from CD45+ TCL. The pathologists were blinded to the flow cytometry findings. Outcome information was sought for the 20 dogs with CD45- lymphoma, and population characteristics of the additional 494 dogs were described.
Results: All 20 CD45- cases were classified as TZL. The 15 CD45+ cases were classified as aggressive TCL and are described in an accompanying paper. TZL cases had a median survival of 637 days. Examination of 494 additional dogs diagnosed with TZL by immunophenotyping demonstrated that 40% of cases are in Golden Retrievers, are diagnosed at a median age of 10 years, and the majority have lymphadenopathy and lymphocytosis.
Conclusions: TZL has unique immunophenotypic features that can be used for diagnosis.
Keywords: Flow cytometry; Golden retriever; Leukemia.
Copyright © 2014 by the American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Swerdlow DL, Campo E, Harris NL et al., editors. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues 4th ed Geneva: WHO Press; 2008.
-
- de Leval L, Rickman DS, Thielen C, et al. The gene expression profile of nodal peripheral T‐cell lymphoma demonstrates a molecular link between angioimmunoblastic T‐cell lymphoma (AITL) and follicular helper T (TFH) cells. Blood 2007;109:4952–4963. - PubMed
-
- Fielding AK, Banerjee L, Marks DI. Recent developments in the management of T‐cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2012;7:160–169. - PubMed
-
- Valli VE, San Myint M, Barthel A, et al. Classification of canine malignant lymphomas according to the World Health Organization criteria. Vet Pathol 2011;48:198–211. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

