Recurrent aphthous stomatitis
- PMID: 24655523
- PMCID: PMC3964366
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cden.2013.12.002
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis
Abstract
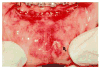
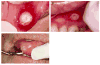
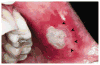
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS) is the most common ulcerative disease affecting the oral mucosa. RAS occurs mostly in healthy individuals and has an atypical clinical presentation in immunocompromised individuals. The etiology of RAS is still unknown, but several local, systemic, immunologic, genetic, allergic, nutritional, and microbial factors, as well as immunosuppressive drugs, have been proposed as causative agents. Clinical management of RAS using topical and systemic therapies is based on severity of symptoms and the frequency, size, and number of lesions. The goals of therapy are to decrease pain and ulcer size, promote healing, and decrease the frequency of recurrence.
Keywords: Aphthous; Behçet disease; Crohn disease; Immunologic; Nutritional deficiency; Psychological stress; Systemic therapy; Topical therapy.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Porter SR, Scully C, Pedersen A. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1998;9(3):306–321. - PubMed
-
- Ship Epidemiologic aspects of recurrent aphthous ulcerations. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1972 Mar;33(3):400–406. - PubMed
-
- Rogers RS., 3rd Recurrent aphthous stomatitis: clinical characteristics and associated systemic disorders. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 1997 Dec;16(4):278–283. - PubMed
-
- Miller MF, Garfunkel AA, Ram CA, Ship The inheritance of recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Observations on susceptibility. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1980 May;49(5):409–412. - PubMed
-
- Crivelli MR, Aguas S, Adler I, Quarracino C, Bazerque P. Influence of socioeconomic status on oral mucosa lesion prevalence in schoolchildren. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 1988 Feb;16(1):58–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

