Sleep-disordered breathing in patients with heart failure
- PMID: 24656103
- PMCID: PMC3964361
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hfc.2013.10.001
Sleep-disordered breathing in patients with heart failure
Abstract
Sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) is prevalent in patients with heart failure, and is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. SDB is proinflammatory, with nocturnal oxygen desaturations and hypercapnia appearing to play a pivotal role in the development of oxidative stress and sympathetic activation. Preliminary data suggest that attention to the diagnosis and management of SDB in patients with heart failure may improve outcomes. Ongoing research into the roles of comorbidities such as SDB as a treatment target may lead to better clinical outcomes and improved quality of life for patients with heart failure.
Keywords: Adaptive servoventilation; Clinical trials; Comorbidities; Heart failure; Outcomes; Positive airway pressure; Sleep apnea.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
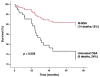
References
-
- Massie BM, O’Connor CM, Metra M, et al. Rolofylline, an adenosine A1-receptor antagonist, in acute heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(15):1419–1428. - PubMed
-
- Gheorghiade M, Bohm M, Greene SJ, et al. Effect of aliskiren on postdischarge mortality and heart failure readmissions among patients hospitalized for heart failure: the ASTRONAUT randomized trial. JAMA. 2013;309(11):1125–1135. - PubMed
-
- Swedberg K, Young JB, Anand IS, et al. Treatment of anemia with darbepoetin alfa in systolic heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(13):1210–1219. - PubMed
-
- Felker GM, Pang PS, Adams KF, et al. Clinical Trials of Pharmacological Therapies in Acute Heart Failure Syndromes: Lessons Learned and Directions Forward. Circ Heart Fail. 2010;3(2):314–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

