Systematic identification of regulatory elements in conserved 3' UTRs of human transcripts
- PMID: 24656821
- PMCID: PMC4430845
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.03.001
Systematic identification of regulatory elements in conserved 3' UTRs of human transcripts
Abstract
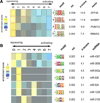
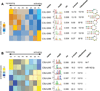
Posttranscriptional regulatory programs governing diverse aspects of RNA biology remain largely uncharacterized. Understanding the functional roles of RNA cis-regulatory elements is essential for decoding complex programs that underlie the dynamic regulation of transcript stability, splicing, localization, and translation. Here, we describe a combined experimental/computational technology to reveal a catalog of functional regulatory elements embedded in 3' UTRs of human transcripts. We used a bidirectional reporter system coupled with flow cytometry and high-throughput sequencing to measure the effect of short, noncoding, vertebrate-conserved RNA sequences on transcript stability and translation. Information-theoretic motif analysis of the resulting sequence-to-gene-expression mapping revealed linear and structural RNA cis-regulatory elements that positively and negatively modulate the posttranscriptional fates of human transcripts. This combined experimental/computational strategy can be used to systematically characterize the vast landscape of posttranscriptional regulatory elements controlling physiological and pathological cellular state transitions.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

