Novel hexadentate and pentadentate chelators for ⁶⁴Cu-based targeted PET imaging
- PMID: 24657050
- PMCID: PMC4139964
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2014.02.041
Novel hexadentate and pentadentate chelators for ⁶⁴Cu-based targeted PET imaging
Abstract
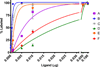
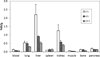
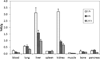
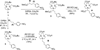
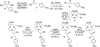
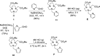
A series of new hexadentate and pentadentate chelators were designed and synthesized as chelators of (64)Cu. The new pentadentate and hexadentate chelators contain different types of donor groups and are expected to form neutral complexes with Cu(II). The new chelators were evaluated for complex kinetics and stability with (64)Cu. The new chelators instantly bound to (64)Cu with high labeling efficiency and maximum specific activity. All (64)Cu-radiolabeled complexes in human serum remained intact for 2 days. The (64)Cu-radiolabeled complexes were further challenged by EDTA in a 100-fold molar excess. Among the (64)Cu-radiolabeled complexes evaluated, (64)Cu-complex of the new chelator E was well tolerated with a minimal transfer of (64)Cu to EDTA. (64)Cu-radiolabeled complex of the new chelator E was further evaluated for biodistribution studies using mice and displayed rapid blood clearance and low organ uptake. (64)Cu-chelator E produced a favorable in vitro and in vivo complex stability profiles comparable to (64)Cu complex of the known hexadentate NOTA chelator. The in vitro and in vivo data highlight strong potential of the new chelator E for targeted PET imaging application.
Keywords: (64)Cu; Chelating agents; NOTA; PET imaging.
Copyright © 2014. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
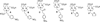

Similar articles
-
Promising bifunctional chelators for copper 64-PET imaging: practical (64)Cu radiolabeling and high in vitro and in vivo complex stability.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2016 Apr;21(2):177-84. doi: 10.1007/s00775-015-1318-7. Epub 2015 Dec 14. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2016. PMID: 26666778 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of (64)Cu-complexing bifunctional chelators for radioimmunoconjugation: labeling efficiency, specific activity, and in vitro/in vivo stability.Bioconjug Chem. 2012 May 16;23(5):1029-39. doi: 10.1021/bc300037w. Epub 2012 Apr 13. Bioconjug Chem. 2012. PMID: 22471317 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Evaluation of New Generation Cross-Bridged Bifunctional Chelator for (64)Cu Radiotracers.Inorg Chem. 2015 Sep 8;54(17):8177-86. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.5b01386. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Inorg Chem. 2015. PMID: 26286436
-
Chelators for copper radionuclides in positron emission tomography radiopharmaceuticals.J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2014 Apr;57(4):224-30. doi: 10.1002/jlcr.3165. Epub 2013 Dec 18. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2014. PMID: 24347474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging chelators for nuclear imaging.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2021 Aug;63:152-162. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2021.03.001. Epub 2021 May 26. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 34051509 Review.
Cited by
-
Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Vessel Wall Matrix Metalloproteinase Activity in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023 Jan;16(1):e014615. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.122.014615. Epub 2023 Jan 17. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36649454 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Cu-64 and Ga-68 Radiolabeled Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists as PET Tracers for Pancreatic β cell Imaging.Mol Imaging Biol. 2016 Feb;18(1):90-8. doi: 10.1007/s11307-015-0861-5. Mol Imaging Biol. 2016. PMID: 25987465 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of 64Cu-Based Radiopharmaceuticals that Target Aβ Peptide Aggregates as Diagnostic Tools for Alzheimer's Disease.J Am Chem Soc. 2017 Sep 13;139(36):12550-12558. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b05937. Epub 2017 Aug 29. J Am Chem Soc. 2017. PMID: 28823165 Free PMC article.
-
Metals in Imaging of Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 2;21(23):9190. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239190. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33276505 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

