Environmentally induced epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of disease susceptibility
- PMID: 24657180
- PMCID: PMC4148471
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trsl.2014.02.003
Environmentally induced epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of disease susceptibility
Abstract
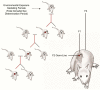
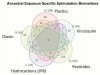
Environmental insults, such as exposure to toxicants or nutritional abnormalities, can lead to epigenetic changes that are in turn related to increased susceptibility to disease. The focus of this review is on the transgenerational inheritance of such epigenetic abnormalities (epimutations), and how it is that these inherited epigenetic abnormalities can lead to increased disease susceptibility, even in the absence of continued environmental insult. Observations of environmental toxicant specificity and exposure-specific disease susceptibility are discussed. How epimutations are transmitted across generations and how epigenetic changes in the germline are translated into an increased disease susceptibility in the adult is reviewed with regard to disease etiology.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distinctions between transgenerational and non-transgenerational epimutations.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014 Dec;398(1-2):13-23. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2014.07.016. Epub 2014 Jul 28. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 25079508 Review.
-
Genome-Wide Locations of Potential Epimutations Associated with Environmentally Induced Epigenetic Transgenerational Inheritance of Disease Using a Sequential Machine Learning Prediction Approach.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 16;10(11):e0142274. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142274. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26571271 Free PMC article.
-
Environmentally Induced Epigenetic Transgenerational Inheritance of Reproductive Disease.Biol Reprod. 2015 Dec;93(6):145. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.115.134817. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Biol Reprod. 2015. PMID: 26510870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmentally induced epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of sperm epimutations promote genetic mutations.Epigenetics. 2015;10(8):762-71. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1062207. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 26237076 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of parent-of-origin allelic transmission of outcross pathology and sperm epimutations.Dev Biol. 2020 Feb 1;458(1):106-119. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2019.10.030. Epub 2019 Nov 1. Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 31682807 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
DNA methylation in Huntington's disease: Implications for transgenerational effects.Neurosci Lett. 2016 Jun 20;625:34-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.10.060. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Neurosci Lett. 2016. PMID: 26522374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An assessment of molecular pathways of obesity susceptible to nutrient, toxicant and genetically induced epigenetic perturbation.J Nutr Biochem. 2016 Apr;30:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Oct 23. J Nutr Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27012616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmentally toxicant exposures induced intragenerational transmission of liver abnormalities in mice.Open Vet J. 2017;7(3):244-253. doi: 10.4314/ovj.v7i3.8. Epub 2017 Aug 19. Open Vet J. 2017. PMID: 28884077 Free PMC article.
-
Paternal bisphenol A exposure induces testis and sperm pathologies in mice offspring: Possibly due to oxidative stress?Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021 Jan;28(1):948-955. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.11.003. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33424387 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals, Transgenerational Epigenetics and Metabolic Diseases.EC Endocrinol Metab Res. 2017 Nov;21:31-51. EC Endocrinol Metab Res. 2017. PMID: 34734213 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pembrey ME. Male-line transgenerational responses in humans. Hum Fertil (Camb) 2010;13:268–271. - PubMed
-
- Drake AJ, Walker BR, Seckl JR. Intergenerational consequences of fetal programming by in utero exposure to glucocorticoids in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005;288:R34–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

