miR-34: from bench to bedside
- PMID: 24657911
- PMCID: PMC4011589
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.1825
miR-34: from bench to bedside
Abstract
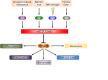
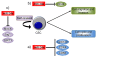
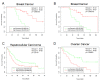
The mir-34 family was originally cloned and characterized in 2007 as a p53 target gene. Almost immediately it became clear that its major role is as a master regulator of tumor suppression. Indeed, when overexpressed, it directly and indirectly represses several oncogenes, resulting in an increase of cancer cell death (including cancer stem cells), and in an inhibition of metastasis. Moreover, its expression is deregulated in several human cancers. In 2013, a miR-34 mimic has become the first microRNA to reach phase 1 clinical trials. Here we review the miR-34 family and their role in tumor biology, and discuss the potential therapeutic applications of miR-34a mimic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-34a: a novel tumor suppressor in p53-mutant glioma cell line U251.Arch Med Res. 2010 Feb;41(2):67-74. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2010.02.007. Arch Med Res. 2010. PMID: 20470934
-
Transcriptome-wide characterization of the endogenous miR-34A-p53 tumor suppressor network.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 2;7(31):49611-49622. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10417. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27391063 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative mechanisms of miR-34a regulation in cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Oct 12;8(10):e3100. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.495. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 29022903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-34a inhibits migration and invasion of colon cancer cells via targeting to Fra-1.Carcinogenesis. 2012 Mar;33(3):519-28. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgr304. Epub 2011 Dec 22. Carcinogenesis. 2012. PMID: 22198213
-
Mutant p53 exerts oncogenic effects through microRNAs and their target gene networks.FEBS Lett. 2014 Aug 19;588(16):2610-5. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.03.054. Epub 2014 Apr 12. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24726728 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-497 and miR-34a retard lung cancer growth by co-inhibiting cyclin E1 (CCNE1).Oncotarget. 2015 May 30;6(15):13149-63. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3693. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25909221 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-34a suppresses amphiregulin and tumor metastatic potential of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC).Oncotarget. 2015 Apr 10;6(10):7454-69. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3148. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25762634 Free PMC article.
-
The novel role of miRNAs for tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Jul;72(13):2575-84. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1887-1. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25782411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A genetically engineered microRNA-34a prodrug demonstrates anti-tumor activity in a canine model of osteosarcoma.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 31;13(12):e0209941. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209941. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30596759 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of non-coding RNAs in regulating cancer drug targets.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022 Mar 25;54(3):279-291. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2022006. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022. PMID: 35538038 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stefani G, Slack FJ. Small non-coding RNAs in animal development. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology. 2008;9(3):219–230. - PubMed
-
- Garzon R, Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNAs in Cancer. Annual review of medicine. 2009;60:167–179. - PubMed
-
- Hermeking H. The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17(2):193–199. - PubMed
-
- Kinoshita T, Hanazawa T, Nohata N, Kikkawa N, Enokida H, Yoshino H, Yamasaki T, Hidaka H, Nakagawa M, Okamoto Y, Seki N. Tumor suppressive microRNA-218 inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion through targeting laminin-332 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2012;3(11):1386–1400. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

