3-Methylcholanthrene, an AhR agonist, caused cell-cycle arrest by histone deacetylation through a RhoA-dependent recruitment of HDAC1 and pRb2 to E2F1 complex
- PMID: 24658119
- PMCID: PMC3962457
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092793
3-Methylcholanthrene, an AhR agonist, caused cell-cycle arrest by histone deacetylation through a RhoA-dependent recruitment of HDAC1 and pRb2 to E2F1 complex
Abstract
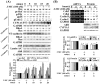
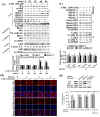
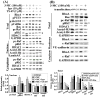
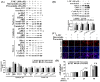
We previously showed that treating vascular endothelial cells with 3-methylcholanthrene (3MC) caused cell-cycle arrest in the Go/G1 phase; this resulted from the induction of p21 and p27 and a decreased level and activity of the cyclin-dependent kinase, Cdk2. We further investigated the molecular mechanisms that modulate cell-cycle regulatory proteins through the aryl-hydrocarbon receptor (AhR)/Ras homolog gene family, member A (RhoA) dependent epigenetic modification of histone. AhR/RhoA activation mediated by 3MC was essential for the upregulation of retinoblastoma 2 (pRb2) and histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1), whereas their nuclear translocation was primarily modulated by RhoA activation. The combination of increased phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) activity and decreased phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) activation by 3MC led to the inactivation of the Ras-cRaf pathway, which contributed to pRb2 hypophosphorylation. Increased HDAC1/pRb2 recruitment to the E2F1 complex decreased E2F1-transactivational activity and H3/H4 deacetylation, resulting in the downregulation of cell-cycle regulatory proteins (Cdk2/4 and Cyclin D3/E). Co-immunoprecipitation and electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) results showed that simvastatin prevented the 3MC-increased binding activities of E2F1 proteins in their promoter regions. Additionally, RhoA inhibitors (statins) reversed the effect of 3MC in inhibiting DNA synthesis by decreasing the nuclear translocation of pRb2/HDAC1, leading to a recovery of the levels of cell-cycle regulatory proteins. In summary, 3MC decreased cell proliferation by the epigenetic modification of histone through an AhR/RhoA-dependent mechanism that can be rescued by statins.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
RhoA-mediated inhibition of vascular endothelial cell mobility: positive feedback through reduced cytosolic p21 and p27.J Cell Physiol. 2014 Oct;229(10):1455-65. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24583. J Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24535918
-
Mediating effects of aryl-hydrocarbon receptor and RhoA in altering brain vascular integrity: the therapeutic potential of statins.Am J Pathol. 2012 Jul;181(1):211-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.03.032. Am J Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22720799
-
Molecular mechanisms of p21 and p27 induction by 3-methylcholanthrene, an aryl-hydrocarbon receptor agonist, involved in antiproliferation of human umbilical vascular endothelial cells.J Cell Physiol. 2008 Apr;215(1):161-71. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21299. J Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18022818
-
Simvastatin reduces the carcinogenic effect of 3-methylcholanthrene in renal epithelial cells through histone deacetylase 1 inhibition and RhoA reactivation.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 14;9(1):4606. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40757-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30872677 Free PMC article.
-
Gene methylation in gastric cancer.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Sep 23;424:53-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 May 10. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23669186 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Agonist Suppresses Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 1;11(12):e0167650. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167650. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27907195 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Methylation Patterns in T Cells of Naïve and Influenza A Virus-Infected Mice Developmentally Exposed to an Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Ligand.Environ Health Perspect. 2021 Jan;129(1):17007. doi: 10.1289/EHP7699. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Environ Health Perspect. 2021. PMID: 33449811 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis Induction byHistone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Cancer Cells: Role of Ku70.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 30;20(7):1601. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071601. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30935057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway: a linking bridge between the gut microbiome and neurodegenerative diseases.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Aug 8;18:1433747. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1433747. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39175504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The complex biology of aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation in cancer and beyond.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Oct;216:115798. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115798. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37696456 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ma Q, Whitlock JP Jr (1997) A novel cytoplasmic protein that interacts with the Ah receptor, contains tetratricopeptide repeat motifs, and augments the transcriptional response to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Biol Chem 272: 8878–8884. - PubMed
-
- Denison MS, Whitlock JP Jr (1995) Xenobiotic-inducible transcription of cytochrome P450 genes. J Biol Chem 270: 18175–18178. - PubMed
-
- Pang PH, Lin YH, Lee YH, Hou HH, Hsu SP, et al. (2008) Molecular mechanisms of p21 and p27 induction by 3-methylcholanthrene, an aryl-hydrocarbon receptor agonist, involved in antiproliferation of human umbilical vascular endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol 215: 161–171. - PubMed
-
- Chang CC, Lee PS, Chou Y, Hwang LL, Juan SH (2012) Mediating effects of aryl-hydrocarbon receptor and RhoA in altering brain vascular integrity: the therapeutic potential of statins. Am J Pathol 181: 211–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

