Stercoral perforation in a child: a rare complication of NSAID use
- PMID: 24658528
- PMCID: PMC3962979
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2014-203652
Stercoral perforation in a child: a rare complication of NSAID use
Abstract
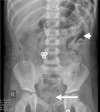
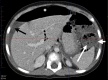
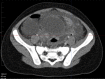
The adverse effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) on the gastrointestinal (GI) tract are well known. However, NSAID use rarely leads to a stercoral perforation, an extremely rare but life-threatening cause of acute abdomen. We present a case of stercoral sigmoid colon perforation in a 2-year-old girl, secondary to unintentional NSAID overdose, developing as a result of miscommunication between the general practitioner (GP) and the mother. To the best of our knowledge, stercoral perforation has never before been reported in a child.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and stercoral perforation of the colon.Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1991 Nov;73(6):337-9; discussion 339-40. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1991. PMID: 1759759 Free PMC article.
-
Case reports. Stercoral perforation of the sigmoid colon: computed tomography findings.Clin Radiol. 2000 Sep;55(9):727-9. doi: 10.1053/crad.1999.0173. Clin Radiol. 2000. PMID: 10988058 Review. No abstract available.
-
Stercoral Perforation of the Colon: A Potentially Fatal Complication of Opioid-Induced Constipation.J Pain Symptom Manage. 2015 Aug;50(2):260-2. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2015.02.019. Epub 2015 Apr 3. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2015. PMID: 25847850
-
Stercoral perforation of the sigmoid colon.Br J Surg. 1973 Jan;60(1):61-3. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800600117. Br J Surg. 1973. PMID: 4685924 No abstract available.
-
Imaging manifestations of faecal impaction and stercoral perforation.Clin Radiol. 2011 Jan;66(1):83-8. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2010.08.002. Clin Radiol. 2011. PMID: 21147303 Review.
Cited by
-
Stercoral Colitis in a Patient With Pediatric-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Case Analysis and Review of the Literature.Front Pediatr. 2021 Oct 27;9:760517. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.760517. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34778151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allison MC, Howatson AG, Torrance CJ, et al. Gastrointestinal damage associated with the use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. N Engl J Med 1992;327:749–54 - PubMed
-
- Laine L, Curtis SP, Langman M, et al. Lower gastrointestinal events in a double-blind trial of the cyclo-oxygenase-2 selective inhibitor etoricoxib and the traditional nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac. Gastroenterology 2008;135:1517–25 - PubMed
-
- Laine L, Smith R, Min K, et al. Systematic review: the lower gastrointestinal adverse effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2006;24:751–67 - PubMed
-
- Sostres C, Gargallo CJ, Arroyo MT, et al. Adverse effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, aspirin and coxibs) on upper gastrointestinal tract. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2010;24:121–32 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
