Synthesis, docking study and β-adrenoceptor activity of some new oxime ether derivatives
- PMID: 24658567
- PMCID: PMC6271474
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules19033417
Synthesis, docking study and β-adrenoceptor activity of some new oxime ether derivatives
Abstract
A new series of oxime ethers 4a-z was designed and synthesized to test the blocking activity against β₁ and β₂-adrenergic receptors. Docking of these ether derivatives into the active site of the identified 3D structures of β₁ and β₂-adrenergic receptors showed MolDock scores comparable to those of reference compounds. Biological results revealed that the inhibition effects on the heart rate and contractility are less than those of propranolol. Nevertheless, the two compounds 4p and 4q that displayed the highest negative MolDock score with β₂-adrenergic receptors showed β₂-antagonistic activity by decreasing salbutamol relaxation of precontracted tracheal strips, which indicates the importance of a chlorothiophene moiety in the hydrophobic region for best complementarity with β₂ receptors. On other hand, the presence of a homoveratryl moiety increases the MolDock score of the tested compounds with the β₁ receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare in connection with the contents of this manuscript.
Figures
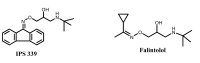


Similar articles
-
Synthesis and beta-adrenergic blocking activity of new aliphatic and alicyclic oxime ethers.J Med Chem. 1984 Oct;27(10):1291-4. doi: 10.1021/jm00376a011. J Med Chem. 1984. PMID: 6148422
-
Synthesis and adrenergic activity of a new series of N-aryl dicyclopropyl ketone oxime ethers: SAR and stereochemical aspects.J Med Chem. 1998 May 7;41(10):1613-8. doi: 10.1021/jm970338c. J Med Chem. 1998. PMID: 9572886
-
Synthesis and beta-adrenergic blocking activity of new aliphatic oxime ethers.J Med Chem. 1980 Jun;23(6):620-4. doi: 10.1021/jm00180a007. J Med Chem. 1980. PMID: 6104730
-
Supramolecular chiro-biomedical aspect of β-blockers in drug development.Curr Drug Targets. 2014;15(7):729-41. doi: 10.2174/1389450115666140429104516. Curr Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 24856145 Review.
-
Human heart beta-adrenoceptors: beta1-adrenoceptor diversification through 'affinity states' and polymorphism.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007 Oct;34(10):1020-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2007.04730.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17714089 Review.
Cited by
-
A new oxime synthesized from Senecio nutans SCh. Bip (chachacoma) reduces calcium influx in the vascular contractile response in rat aorta.RSC Adv. 2024 Mar 25;14(14):9933-9942. doi: 10.1039/d4ra01058b. eCollection 2024 Mar 20. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38528924 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolites Isolated from Senecio nutans Sch. Bip and Their Synthesized Oximes Inhibit Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Activity in Vascular Smooth Muscle.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 17;26(8):3786. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083786. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332402 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of β1- and β2-Adrenergic Receptor Modulators through Advanced Pharmacoinformatics and Machine Learning Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 17;22(20):11191. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011191. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681845 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Biologically Active Oxime Ethers.Molecules. 2023 Jun 28;28(13):5041. doi: 10.3390/molecules28135041. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37446703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ligand-induced conformational changes in the β1-adrenergic receptor revealed by hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 18;15(1):8993. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53161-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39424782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoffman B.B. Adrenoceptor antagonist drugs. In: Katzung B.G., editor. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. 10th ed. McGraw-Hill; New York, NY, USA: 2007.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

