Synthesis of new 2,5-di-substituted 1,3,4-oxadiazoles bearing 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol moieties and evaluation of their antioxidant activity
- PMID: 24658568
- PMCID: PMC6271237
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules19033436
Synthesis of new 2,5-di-substituted 1,3,4-oxadiazoles bearing 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol moieties and evaluation of their antioxidant activity
Abstract
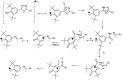
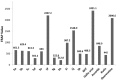
Eleven new 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(5-aryl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)phenols 5a-k were synthesized by reacting aryl hydrazides with 3,5-di-tert butyl 4-hydroxybenzoic acid in the presence of phosphorus oxychloride. The resulting compounds were characterized based on their IR, ¹H-NMR, ¹³C-NMR, and HRMS data. 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazide (DPPH) and ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assays were used to test the antioxidant properties of the compounds. Compounds 5f and 5j exhibited significant free-radical scavenging ability in both assays.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Synthesis and antioxidant activities of acetamidomethylsulfonyl bis heterocycles-oxazolyl/thiazolyl/imidazolyl-1,3,4-oxadiazoles.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2013 Jul;346(7):511-20. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201300115. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2013. PMID: 23801190
-
Design and one-pot and microwave-assisted synthesis of 2-amino/5-aryl-1,3,4-oxadiazoles bearing a benzimidazole moiety as antioxidants.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2012 Jul;345(7):549-56. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201100440. Epub 2012 Mar 30. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2012. PMID: 22467524
-
Screening and evaluation of antioxidant activity of some 1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a]quinazoline derivatives.Future Med Chem. 2018 Feb;10(4):379-390. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2017-0224. Epub 2017 Nov 17. Future Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29145730
-
Synthesis and antioxidant activity of styrylsulfonylmethyl 1,3,4-oxadiazoles, pyrazolyl/isoxazolyl-1,3,4-oxadiazoles.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2013;61(12):1291-7. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c13-00652. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2013. PMID: 24292790
-
Analytical Methods Used in Determining Antioxidant Activity: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 25;22(7):3380. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073380. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33806141 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rational Design and Synthesis of New, High Efficiency, Multipotent Schiff Base-1,2,4-triazole Antioxidants Bearing Butylated Hydroxytoluene Moieties.Molecules. 2016 Jun 28;21(7):847. doi: 10.3390/molecules21070847. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27367658 Free PMC article.
-
Gastroprotective activity of a novel Schiff base derived dibromo substituted compound against ethanol-induced acute gastric lesions in rats.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019 Feb 15;20(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s40360-019-0292-z. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019. Retraction in: BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2024 Oct 16;25(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s40360-024-00801-2. PMID: 30770761 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
New Hydrazones Bearing Thiazole Scaffold: Synthesis, Characterization, Antimicrobial, and Antioxidant Investigation.Molecules. 2015 Sep 18;20(9):17325-38. doi: 10.3390/molecules200917325. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26393564 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation state-dependent modulation of spinal glycine receptors alleviates inflammatory pain.J Clin Invest. 2016 Jul 1;126(7):2547-60. doi: 10.1172/JCI83817. Epub 2016 Jun 6. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 27270175 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo acute toxicity and anti-gastric evaluation of a novel dichloro Schiff base: Bax and HSP70 alteration.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2020 Jan 2;52(1):26-37. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmz140. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2020. PMID: 31889181 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

