Authentication of Bulbus Fritillariae Cirrhosae by RAPD-derived DNA markers
- PMID: 24658569
- PMCID: PMC6271880
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules19033450
Authentication of Bulbus Fritillariae Cirrhosae by RAPD-derived DNA markers
Abstract
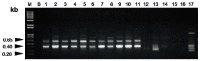
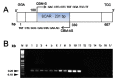
Bulbus Fritillariae is the most commonly used antitussive herb in China. Eleven species of Fritillaria are recorded as Bulbus Fritillariae in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Bulbus Fritillariae Cirrhosae is a group of six Fritillaria species with higher efficiency and lower toxicity derived mainly from wild sources. Because of their higher market price, five other Fritillaria species are often sold deceptively as Bulbus Fritillariae Cirrhosae in the herbal market. To ensure the efficacy and safety of medicinal herbs, the authentication of botanical resources is the first step in quality control. Here, a DNA based identification method was developed to authenticate the commercial sources of Bulbus Fritillariae Cirrhosae. A putative DNA marker (0.65 kb) specific for Bulbus Fritillariae Cirrhosae was identified using the Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) technique. A DNA marker representing a Sequence Characterized Amplified Region (SCAR) was developed from a RAPD amplicon. The SCAR marker was successfully applied to differentiate Bulbus Fritillariae Cirrhosae from different species of Fritillaria. Additionally, the SCAR marker was also useful in identifying the commercial samples of Bulbus Fritillariae Cirrhosae. Our results indicated that the RAPD-SCAR method was rapid, accurate and applicable in identifying Bulbus Fritillariae Cirrhosae at the DNA level.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Simultaneous identification of Bulbus Fritillariae cirrhosae using PCR-RFLP analysis.Phytomedicine. 2007 Sep;14(9):628-32. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2006.09.008. Epub 2007 Mar 1. Phytomedicine. 2007. PMID: 17336047
-
Combining DNA Barcoding and HPLC Fingerprints to Trace Species of an Important Traditional Chinese Medicine Fritillariae Bulbus.Molecules. 2019 Sep 8;24(18):3269. doi: 10.3390/molecules24183269. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31500338 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of ITS1 haplotypes of Fritillariae Cirrhosae Bulbus by amplicon sequencing.Chin Med. 2024 Feb 28;19(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00911-3. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38419104 Free PMC article.
-
[Research progress on resources in Bulbus Fritillariae Cirrhosae].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2008 Jul;33(14):1645-8. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18841756 Review. Chinese.
-
Application of Analytical Technologies in the Discrimination and Authentication of Herbs from Fritillaria: A Review.Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2024;54(6):1775-1796. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2022.2132374. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 36227577 Review.
Cited by
-
Authentication of Acori Tatarinowii Rhizoma (Shi Chang Pu) and its adulterants by morphological distinction, chemical composition and ITS sequencing.Chin Med. 2016 Sep 26;11:41. doi: 10.1186/s13020-016-0113-x. eCollection 2016. Chin Med. 2016. PMID: 27708691 Free PMC article.
-
SCAR marker for identification and discrimination of specific medicinal Lycium chinense Miller from Lycium species from ramp-PCR RAPD fragments.3 Biotech. 2020 Aug;10(8):334. doi: 10.1007/s13205-020-02325-y. Epub 2020 Jul 6. 3 Biotech. 2020. PMID: 32656067 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of four B-chromosome-specific RAPDs and the development of SCAR markers on the maize B-chromosome.Mol Genet Genomics. 2015 Apr;290(2):431-41. doi: 10.1007/s00438-014-0926-1. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Mol Genet Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25258187
-
Rapid Authentication of the Herbal Medicine Plant Species Aralia continentalis Kitag. and Angelica biserrata C.Q. Yuan and R.H. Shan Using ITS2 Sequences and Multiplex-SCAR Markers.Molecules. 2016 Feb 29;21(3):270. doi: 10.3390/molecules21030270. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 26938512 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Authentication of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis var. grandiflora Nakai by Improved RAPD-Derived DNA Markers.Molecules. 2015 Nov 10;20(11):20219-29. doi: 10.3390/molecules201119687. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26569205 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The State Pharmacopoeia Commission of the People’s Republic of China . Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. 2010 ed. Volume 1. Chemical Industry Press; Beijing, China: 2010. p. 191.
-
- Chan S.W., Li S.L., Lin G., Li P. Pharmacokinetic study and determination of imperialine, the major bioactive component in antitussive Fritillaria cirrhosa, in rat by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with evaporative light-scattering detector. Anal. Biochem. 2000;285:172–175. doi: 10.1006/abio.2000.4756. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yu X.L., Ji H., Wang C.L., Li P. Survey of pharmacology researches of Bulbus Fritillariae. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 2000;31:313–315.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

