Serum vascular endothelial growth factor, transforming growth factor β1, and nitric oxide levels in patients with psoriasis vulgaris: their correlation to disease severity
- PMID: 24659464
- PMCID: PMC6807330
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.21717
Serum vascular endothelial growth factor, transforming growth factor β1, and nitric oxide levels in patients with psoriasis vulgaris: their correlation to disease severity
Abstract
Background: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1), and nitric oxide (NO) have been reported to be contributory factors to the pathogenesis of psoriasis vulgaris. In the current study, we aimed to investigate the association between the levels of VEGF, TGF-β1, and NO and psoriasis severity (as expressed by psoriasis area severity index, PASI).
Methods: Fifty-eight patients with psoriasis vulgaris and twenty-two controls were included in the study. The serum levels of VEGF and TGF-β1 were estimated by ELISA technique. The serum levels of NO were determined by colorimetric method.
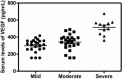
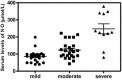
Results: The serum levels of VEGF, TGF-β1, and NO were significantly higher in patients than controls. Moreover, the serum levels of the studied biochemical variables in patients with severe disease activity were significantly higher than mild cases. The duration of disease showed significant positive correlations with each VEGF (r = 0.35, P < 0.01) and TGF-β1 (r = 0.41, P < 0.05). In addition, the PASI score was significantly positively correlated with VEGF (r = 0.65, P < 0.001), TGF-β1 (r = 0.31, P < 0.05), and NO (r = 0.51, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: These findings suggest an association between psoriasis disease severity and serum levels of VEGF, TGF-β1, and NO, which can be recognized as markers of the psoriasis severity. The modulation of their production may represent a therapeutic potential strategy for psoriasis.
Keywords: NO; TGF-β1; VEGF; patients; psoriasis vulgaris.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Simonetti O, Lucarini G, Goteri G, et al. VEGF is likely a key factor in the link between inflammation and angiogenesis in psoriasis: Results of an immunohistochemical study. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 2006;19:751–760. - PubMed
-
- Henno A, Blacher S, Lambert CA, et al. Histological and transcriptional study of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in uninvolved skin, acute pinpoint lesions and established psoriasis plaques: An approach of vascular development chronology in psoriasis. J Dermatol Sci 2010;57:162–169. - PubMed
-
- Micali G, Lacarrubba F, Musumeci ML, Massimino D, Nasca MR. Cutaneous vascular patterns in psoriasis. Int J Dermatol 2010;49(3):249–256. - PubMed
-
- Keck PJ, Hauser SD, Krivi G, et al. Vascular permeability factor, an endothelial cell mitogen related to PDGF. Science 1989;246:1309–1312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

