Gene regulatory cascade of senescence-associated NAC transcription factors activated by ETHYLENE-INSENSITIVE2-mediated leaf senescence signalling in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 24659488
- PMCID: PMC4106440
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/eru112
Gene regulatory cascade of senescence-associated NAC transcription factors activated by ETHYLENE-INSENSITIVE2-mediated leaf senescence signalling in Arabidopsis
Abstract
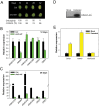
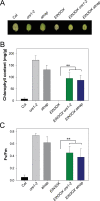
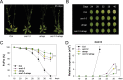
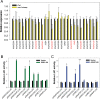
Leaf senescence is a finely tuned and genetically programmed degeneration process, which is critical to maximize plant fitness by remobilizing nutrients from senescing leaves to newly developing organs. Leaf senescence is a complex process that is driven by extensive reprogramming of global gene expression in a highly coordinated manner. Understanding how gene regulatory networks involved in controlling leaf senescence are organized and operated is essential to decipher the mechanisms of leaf senescence. It was previously reported that the trifurcate feed-forward pathway involving EIN2, ORE1, and miR164 in Arabidopsis regulates age-dependent leaf senescence and cell death. Here, new components of this pathway have been identified, which enhances knowledge of the gene regulatory networks governing leaf senescence. Comparative gene expression analysis revealed six senescence-associated NAC transcription factors (TFs) (ANAC019, AtNAP, ANAC047, ANAC055, ORS1, and ORE1) as candidate downstream components of ETHYLENE-INSENSITIVE2 (EIN2). EIN3, a downstream signalling molecule of EIN2, directly bound the ORE1 and AtNAP promoters and induced their transcription. This suggests that EIN3 positively regulates leaf senescence by activating ORE1 and AtNAP, previously reported as key regulators of leaf senescence. Genetic and gene expression analyses in the ore1 atnap double mutant revealed that ORE1 and AtNAP act in distinct and overlapping signalling pathways. Transient transactivation assays further demonstrated that ORE1 and AtNAP could activate common as well as differential NAC TF targets. Collectively, the data provide insight into an EIN2-mediated senescence signalling pathway that coordinates global gene expression during leaf senescence via a gene regulatory network involving EIN3 and senescence-associated NAC TFs.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; EIN2-mediated senescence signalling; EIN3; NAC transcription factor.; gene.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology.
Figures




Similar articles
-
EIN3 and ORE1 Accelerate Degreening during Ethylene-Mediated Leaf Senescence by Directly Activating Chlorophyll Catabolic Genes in Arabidopsis.PLoS Genet. 2015 Jul 28;11(7):e1005399. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005399. eCollection 2015 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26218222 Free PMC article.
-
Ethylene-insensitive3 is a senescence-associated gene that accelerates age-dependent leaf senescence by directly repressing miR164 transcription in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2013 Sep;25(9):3311-28. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.113340. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Plant Cell. 2013. PMID: 24064769 Free PMC article.
-
NAC transcription factor ORE1 and senescence-induced BIFUNCTIONAL NUCLEASE1 (BFN1) constitute a regulatory cascade in Arabidopsis.Mol Plant. 2013 Sep;6(5):1438-52. doi: 10.1093/mp/sst012. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Mol Plant. 2013. PMID: 23340744
-
The role of hormones in the aging of plants - a mini-review.Gerontology. 2014;60(1):49-55. doi: 10.1159/000354334. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Gerontology. 2014. PMID: 24135638 Review.
-
Transcription factors regulating leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2008 Sep;10 Suppl 1:63-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1438-8677.2008.00088.x. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2008. PMID: 18721312 Review.
Cited by
-
EIN3 and ORE1 Accelerate Degreening during Ethylene-Mediated Leaf Senescence by Directly Activating Chlorophyll Catabolic Genes in Arabidopsis.PLoS Genet. 2015 Jul 28;11(7):e1005399. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005399. eCollection 2015 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26218222 Free PMC article.
-
The role of ANAC072 in the regulation of chlorophyll degradation during age- and dark-induced leaf senescence.Plant Cell Rep. 2016 Aug;35(8):1729-41. doi: 10.1007/s00299-016-1991-1. Epub 2016 May 6. Plant Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27154758
-
Signal Transduction in Leaf Senescence: Progress and Perspective.Plants (Basel). 2019 Oct 10;8(10):405. doi: 10.3390/plants8100405. Plants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31658600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Soybean GmNAC019 Transcription Factor Mediates Drought Tolerance in Arabidopsis in an Abscisic Acid-Dependent Manner.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 31;21(1):286. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010286. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31906240 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of the NAC Transcription Factor Gene Family Reveals Differential Expression Patterns and Cold-Stress Responses in the Woody Plant Prunus mume.Genes (Basel). 2018 Oct 12;9(10):494. doi: 10.3390/genes9100494. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30322087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso JM, Hirayama T, Roman G, Nourizadeh S, Ecker JR. 1999. EIN2, a bifunctional transducer of ethylene and stress responses in Arabidopsis . Science 284, 2148–2152 - PubMed
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, et al. 2003. Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301, 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Balazadeh S, Riano-Pachon DM, Mueller-Roeber B. 2008. Transcription factors regulating leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana . Plant Biology (Stuttgart) 10 Suppl 1, 63–75 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

