Validation of the only commercially available immunoassay for synthetic cathinones in urine: Randox Drugs of Abuse V Biochip Array Technology
- PMID: 24659527
- PMCID: PMC4107059
- DOI: 10.1002/dta.1633
Validation of the only commercially available immunoassay for synthetic cathinones in urine: Randox Drugs of Abuse V Biochip Array Technology
Abstract
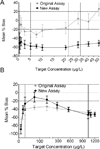
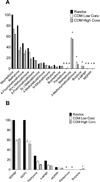
Deterrence of synthetic cathinone abuse is hampered by the lack of a high-throughput immunoassay screen. The Randox Drugs of Abuse V (DOA-V) Biochip Array Technology contains two synthetic cathinone antibodies: Bath Salt I (BSI) targets mephedrone/methcathinone and Bath Salt II (BSII) targets 3',4'-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV)/3',4'-methylenedioxy-α-pyrrolidinobutiophenone (MDPBP). We evaluated DOA-V synthetic cathinones performance and conducted a full validation on the original assay with calibrators reconstituted in water, and the new assay with calibrators prepared in lyophilized urine; both utilized the same antibodies and were run on the fully automated Evidence® Analyzer. We screened 20 017 authentic military urine specimens and confirmed positives by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) for 28 synthetic cathinones. Limits of detection (LOD) for the original and new assays were 0.35 and 0.18 (BSI), and 8.5 and 9.2 µg/L (BSII), respectively. Linearity was acceptable (R(2) >0.98); however, a large negative bias was observed with in-house prepared calibrators. Intra-assay imprecision was <20% BSI-II, while inter-assay imprecision was 18-42% BSI and <22% BSII. Precision was acceptable for Randox controls. Cross-reactivities of many additional synthetic cathinones were determined. Authentic drug-free negative urine pH <4 produced false positive results for BSI (6.3 µg/L) and BSII (473 µg/L). Oxidizing agents reduced BSI and increased BSII results. Sensitivity, specificity, and efficiency of 100%, 52.1%, and 53.0% were obtained at manufacturer's proposed cut-offs (BSI 5 µg/L, BSII 30 µg/L). Performance improved if cut-off concentrations increased (BSI 7.5 µg/L, BSII 40 µg/L); however, there were limited confirmed positive specimens. Currently, this is the first and only fully validated immunoassay for preliminary detection of synthetic cathinones in urine. Published 2014. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Keywords: MDPV; Randox; immunoassay; mephedrone; synthetic cathinones.
Published 2014. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures


References
-
- Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) National Forensic Laboratory Information System Special Report: Synthetic Cannabinoids and Synthetic Cathinones Reported in NFLIS, 2009–2010. 2011.
-
- Peters FT, Meyer MR. In vitro approaches to studying the metabolism of new psychoactive compounds. Drug Test. Anal. 2011;3:483. - PubMed
-
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) Annual Report 2012: The State of the Drugs Problem in Europe. 2012. p. 89.
-
- Zawilska BJ, Wojcieszak J. Designer cathinones--an emerging class of novel recreational drugs. Forensic Sci. Int. 2013;231:42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

