Assessing cellular response to functionalized α-helical peptide hydrogels
- PMID: 24659615
- PMCID: PMC4276410
- DOI: 10.1002/adhm.201400065
Assessing cellular response to functionalized α-helical peptide hydrogels
Abstract
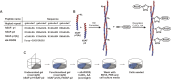
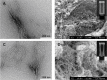
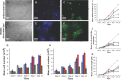
α-Helical peptide hydrogels are decorated with a cell-binding peptide motif (RGDS), which is shown to promote adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation of PC12 cells. Gel structure and integrity are maintained after functionalization. This opens possibilities for the bottom-up design and engineering of complex functional scaffolds for 2D and 3D cell cultures.
Keywords: 2D cell culture; PC12 cells; peptide hydrogels; self-assembled fibers; tissue engineering.
© 2014 The Authors. Published by WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
References
-
- Dhandayuthapani B, Yoshida Y, Maekawa T, Kumar DS. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2011;2011:1.
-
- Jeon O, Song SJ, Lee KJ, Park MH, Lee SH, Hahn SK, Kim S, Kim BS. Carbohyr. Polym. 2007;70:251.
-
- Hou QP, Grijpma DW, Feijen J. Biomaterials. 2003;24:1937. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

