Noncanonical Gβ Gib2 is a scaffolding protein promoting cAMP signaling through functions of Ras1 and Cac1 proteins in Cryptococcus neoformans
- PMID: 24659785
- PMCID: PMC4007421
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.537183
Noncanonical Gβ Gib2 is a scaffolding protein promoting cAMP signaling through functions of Ras1 and Cac1 proteins in Cryptococcus neoformans
Abstract
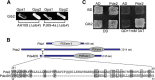
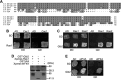
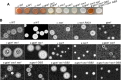
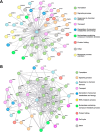
Gβ-like/RACK1 functions as a key mediator of various pathways and contributes to numerous cellular functions in eukaryotic organisms. In the pathogenic fungus Cryptococcus neoformans, noncanonical Gβ Gib2 promotes cAMP signaling in cells lacking normal Gpa1 function while displaying versatility in interactions with Gα Gpa1, protein kinase Pkc1, and endocytic intersectin Cin1. To elucidate the Gib2 functional mechanism(s), we demonstrate that Gib2 is required for normal growth and virulence. We show that Gib2 directly binds to Gpa1 and Gγ Gpg1/Gpg2 and that it interacts with phosphodiesterase Pde2 and monomeric GTPase Ras1. Pde2 remains functionally dispensable, but Ras1 is found to associate with adenylyl cyclase Cac1 through the conserved Ras association domain. In addition, the ras1 mutant exhibits normal capsule formation, whereas the ras1 gpa1 mutant displays enhanced capsule formation, and the ras1 gpa1 cac1 mutant is acapsular. Collectively, these findings suggest that Gib2 promotes cAMP levels by relieving an inhibitory function of Ras1 on Cac1 in the absence of Gpa1. In addition, using GST affinity purification combined with mass spectrometry, we identified 47 additional proteins that interact with Gib2. These proteins have putative functions ranging from signal transduction, energy generation, metabolism, and stress response to ribosomal function. After establishing and validating a protein-protein interactive network, we believe Gib2 to be a key adaptor/scaffolding protein that drives the formation of various protein complexes required for growth and virulence. Our study reveals Gib2 as an essential component in deciphering the complexity of regulatory networks that control growth and virulence in C. neoformans.
Keywords: Adenylate Cyclase (Adenylyl Cyclase); Cyclic AMP (cAMP); Fungal Growth and Virulence; G Proteins; Gβ-like/RACK1; Protein Interactive Network; Ras; Signal Transduction.
Figures




References
-
- Park B. J., Wannemuehler K. A., Marston B. J., Govender N., Pappas P. G., Chiller T. M. (2009) Estimation of the current global burden of cryptococcal meningitis among persons living with HIV/AIDS. AIDS 23, 525–530 - PubMed
-
- Kozel T. R. (1995) Virulence factors of Cryptococcus neoformans. Trends Microbiol. 3, 295–299 - PubMed
-
- Kays A. M., Borkovich K. A. (2004) Signal Transduction Pathways Mediated by Heterotrimeric G Proteins, pp. 175–207, Springer-Verlag, Berlin and Heidelberg
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

