Bowel preparations as quality indicators for colonoscopy
- PMID: 24659866
- PMCID: PMC3961991
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i11.2746
Bowel preparations as quality indicators for colonoscopy
Abstract
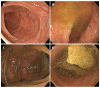
Colonoscopy is the principal investigative procedure for colorectal neoplasms because it can detect and remove most precancerous lesions. The effectiveness of colonoscopy depends on the quality of the examination. Bowel preparation is an essential part of high-quality colonoscopies because only an optimal colonic cleansing allows the colonoscopist to clearly view the entire colonic mucosa and to identify any polyps or other lesions. Suboptimal bowel preparation not only prolongs the overall procedure time, decreases the cecal intubation rate, and increases the costs associated with colonoscopy but also increases the risk of missing polyps or adenomas during the colonoscopy. Therefore, a repeat examination or a shorter colonoscopy follow-up interval may be suitable strategies for a patient with suboptimal bowel preparation.
Keywords: Bower preparation; Colonoscopy; Colorectal neoplasm; Quality.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Ransohoff DF. Colon cancer screening in 2005: status and challenges. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:1685–1695. - PubMed
-
- Winawer S, Fletcher R, Rex D, Bond J, Burt R, Ferrucci J, Ganiats T, Levin T, Woolf S, Johnson D, et al. Colorectal cancer screening and surveillance: clinical guidelines and rationale-Update based on new evidence. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:544–560. - PubMed
-
- Pignone M, Saha S, Hoerger T, Mandelblatt J. Cost-effectiveness analyses of colorectal cancer screening: a systematic review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137:96–104. - PubMed
-
- Farrar WD, Sawhney MS, Nelson DB, Lederle FA, Bond JH. Colorectal cancers found after a complete colonoscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:1259–1264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

