Synthetic triterpenoids can protect against toxicity without reducing the efficacy of treatment with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel in experimental lung cancer
- PMID: 24659938
- PMCID: PMC3960959
- DOI: 10.2203/dose-response.13-018.Liby
Synthetic triterpenoids can protect against toxicity without reducing the efficacy of treatment with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel in experimental lung cancer
Abstract
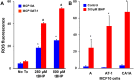
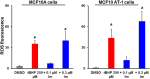
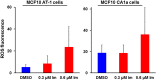
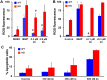
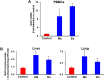
Synthetic oleanane triterpenoids are multifunctional drugs being developed for the prevention and treatment of a variety of chronic diseases driven by inflammation and oxidative stress. Low nanomolar concentrations of triterpenoids inhibit the induction of inflammatory cytokines, and these drugs are potent activators of the Nrf2 cytoprotective pathway. In contrast, low micromolar concentrations of triterpenoids increased the production of ROS and induced apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner in malignant MCF10 CA1a breast cancer cells. Because cancer cells respond differently to ROS than normal cells, it should be possible to exploit these differences therapeutically. In an experimental model of lung cancer, the triterpenoids activated the Nrf2 pathway, as seen by induction of the cytoprotective enzyme NQO1, and reduced the toxicity of carboplatin and paclitaxel. The induction of the Nrf2 pathway in the lung did not suppress the efficacy of treatment with carboplatin and paclitaxel, as the average tumor burden in the group treated with the combination of CDDO-Me and carboplatin/paclitaxel decreased by 90% (P < 0.05 vs. the controls and both single treatment groups). Understanding the dose response of triterpenoids and related drugs will help provide the proper context for optimizing their potential clinical utility.
Keywords: CDDO-Methyl ester; Nrf2; carboplatin toxicity; lung cancer; reactive oxygen species; triterpenoid.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dimethyl fumarate and the oleanane triterpenoids, CDDO-imidazolide and CDDO-methyl ester, both activate the Nrf2 pathway but have opposite effects in the A/J model of lung carcinogenesis.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Jul;36(7):769-81. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv061. Epub 2015 May 4. Carcinogenesis. 2015. PMID: 25939751 Free PMC article.
-
The Triterpenoid CDDO-Methyl Ester Reduces Tumor Burden, Reprograms the Immune Microenvironment, and Protects from Chemotherapy-Induced Toxicity in a Preclinical Mouse Model of Established Lung Cancer.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 May 21;13(6):621. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060621. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929060 Free PMC article.
-
The synthetic triterpenoids, CDDO and CDDO-imidazolide, are potent inducers of heme oxygenase-1 and Nrf2/ARE signaling.Cancer Res. 2005 Jun 1;65(11):4789-98. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4539. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15930299
-
Synthesis and Anticancer Activity of CDDO and CDDO-Me, Two Derivatives of Natural Triterpenoids.Molecules. 2019 Nov 13;24(22):4097. doi: 10.3390/molecules24224097. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31766211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical evidences toward the use of triterpenoid CDDO-Me for solid cancer prevention and treatment.Mol Cancer. 2014 Feb 20;13:30. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-30. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24552536 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer Cell Growth Is Differentially Affected by Constitutive Activation of NRF2 by KEAP1 Deletion and Pharmacological Activation of NRF2 by the Synthetic Triterpenoid, RTA 405.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 24;10(8):e0135257. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135257. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26301506 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Gene Expression Analysis in WM164 Melanoma Cells Revealed That β-β-Dimethylacrylshikonin Leads to ROS Generation, Loss of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential, and Autophagy Induction.Molecules. 2018 Oct 30;23(11):2823. doi: 10.3390/molecules23112823. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30380804 Free PMC article.
-
The PARP inhibitors, veliparib and olaparib, are effective chemopreventive agents for delaying mammary tumor development in BRCA1-deficient mice.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2014 Jul;7(7):698-707. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-14-0047. Epub 2014 May 9. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2014. PMID: 24817481 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics, chemical compositions and biological activities of propolis from Al-Bahah, Saudi Arabia.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 6;7:41453. doi: 10.1038/srep41453. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28165013 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying gene expression patterns associated with drug-specific survival in cancer patients.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 2;11(1):5004. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84211-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33654134 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baird L, Dinkova-Kostova AT. The cytoprotective role of the keap1-nrf2 pathway. Arch Toxicol. 2011;85:241–272. - PubMed
-
- Brookes PS, Morse K, Ray D, Tompkins A, Young SM, Hilchey S, Salim S, Konopleva M, Andreeff M, Phipps R, Bernstein SH. The triterpenoid 2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9-dien-28-oic acid and its derivatives elicit human lymphoid cell apoptosis through a novel pathway involving the unregulated mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Cancer Res. 2007;67:1793–1802. - PubMed
-
- Chauhan D, Li G, Podar K, Hideshima T, Shringarpure R, Catley L, Mitsiades C, Munshi N, Tai YT, Suh N, Gribble GW, Honda T, Schlossman R, Richardson P, Sporn MB, Anderson KC. The bortezomib/proteasome inhibitor PS-341 and triterpenoid CDDO-Im induce synergistic anti-multiple myeloma activity and overcome bortezomib resistance. Blood. 2004;103:3158–3166. - PubMed
-
- Dinkova-Kostova AT, Liby KT, Stephenson KK, Holtzclaw WD, Gao X, Suh N, Williams C, Risingsong R, Honda T, Gribble GW, Sporn MB, Talalay P. Extremely potent triterpenoid inducers of the phase 2 response: Correlations of protection against oxidant and inflammatory stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:4584–4589. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gerlinger M, Rowan AJ, Horswell S, Larkin J, Endesfelder D, Gronroos E, Martinez P, Matthews N, Stewart A, Tarpey P, Varela I, Phillimore B, Begum S, McDonald NQ, Butler A, Jones D, Raine K, Latimer C, Santos CR, Nohadani M, Eklund AC, Spencer-Dene B, Clark G, Pickering L, Stamp G, Gore M, Szallasi Z, Downward J, Futreal PA, Swanton C. Intratumor heterogeneity and branched evolution revealed by multiregion sequencing. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:883–892. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

