S100 protein family in human cancer
- PMID: 24660101
- PMCID: PMC3960449
S100 protein family in human cancer
Abstract
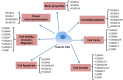
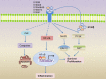
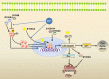
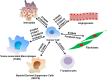
S100 protein family has been implicated in multiple stages of tumorigenesis and progression. Among the S100 genes, 22 are clustered at chromosome locus 1q21, a region frequently rearranged in cancers. S100 protein possesses a wide range of intracellular and extracellular functions such as regulation of calcium homeostasis, cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell invasion and motility, cytoskeleton interactions, protein phosphorylation, regulation of transcriptional factors, autoimmunity, chemotaxis, inflammation and pluripotency. Many lines of evidence suggest that altered expression of S100 proteins was associated with tumor progression and prognosis. Therefore, S100 proteins might also represent potential tumor biomarkers and therapeutic targets. In this review, we summarize the evidence connecting S100 protein family and cancer and discuss the mechanisms by which S100 exerts its diverse functions.
Keywords: S100 proteins; apoptosis; biomarker; invasion; migration; pluripotency; proliferation.
Figures

References
-
- Donato R. S100: a multigenic family of calcium-modulated proteins of the EF-hand type with intracellular and extracellular functional roles. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2001;33:637–668. - PubMed
-
- Heizmann CW, Fritz G, Schafer BW. S100 proteins: structure, functions and pathology. Front Biosci. 2002;7:d1356–1368. - PubMed
-
- Donato R. Perspectives in S-100 protein biology. Review article. Cell Calcium. 1991;12:713–726. - PubMed
-
- Donato R. Functional roles of S100 proteins, calcium-binding proteins of the EF-hand type. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1450:191–231. - PubMed
-
- Donato R. Intracellular and extracellular roles of S100 proteins. Microsc Res Tech. 2003;60:540–551. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
