Tissue plasminogen activator and inflammation: from phenotype to signaling mechanisms
- PMID: 24660119
- PMCID: PMC3960759
Tissue plasminogen activator and inflammation: from phenotype to signaling mechanisms
Abstract
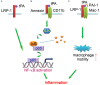
In disease conditions, inflammatory cells, such as neutrophils, T cells, and monocytes/macrophages, are recruited in response to injury cues and express panoply of proinflammatory genes through a combination of transcription factors. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), a member of the serine protease family, has been shown to act as cytokine to activate profound receptor-mediated signaling events. In this review, we will discuss the role of tPA in inflammation in various models, and illuminate its signaling mechanisms underlying its modulation of inflammation.
Keywords: Tissue plasminogen activator; inflammation; phenotype; signaling mechanisms; tPA.
Figures
References
-
- Yee JA, Yan L, Dominguez JC, Allan EH, Martin TJ. Plasminogen-dependent activation of latent transforming growth factor beta (TGF beta) by growing cultures of osteoblast-like cells. J Cell Physiol. 1993;157:528–534. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
