The development and validation of a method using high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) for the qualitative detection of antiretroviral agents in human blood
- PMID: 24661980
- PMCID: PMC4039613
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2014.03.016
The development and validation of a method using high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) for the qualitative detection of antiretroviral agents in human blood
Abstract
Background: Antiretroviral drugs are used for the treatment and prevention of HIV infection. Non-adherence to antiretroviral drug regimens can compromise their clinical efficacy and lead to emergence of drug-resistant HIV. Clinical trials evaluating antiretroviral regimens for HIV treatment and prevention can also be compromised by poor adherence and non-disclosed off-study antiretroviral drug use. This report describes the development and validation of a high throughput, qualitative method for the identification of antiretroviral drugs using high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) for the retrospective assessment of off-study antiretroviral drug use and the determination of potential antiretroviral therapy (ART) non-compliance.
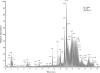
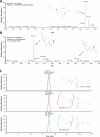
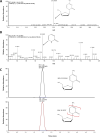
Methods: Serum standards were prepared that contained 15 antiretroviral drugs: 9 protease inhibitors (PIs), 4 nucleotide/nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), and 2 non-nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs). Analytical separation was achieved on a Hypersil Gold PFP (100×3mm) column and the eluent was analyzed using the Thermo Exactive Orbitrap mass spectrometer (Exactive-MS) operated in full scan mode. Limit of identification, signal intensity precision, retention time analysis, selectivity, and carryover studies were conducted. Concordance with liquid chromatographic-tandem mass spectrometric (LC-MS/MS) methods was evaluated using remnant plasma samples from a clinical trial.
Results: The limit of identification ranged from 5 to 10ng/ml for 14 drugs (9 PIs, 1 NNRTI, 4 NRTIs) and was 150ng/ml for 1 NNRTI. Precision studies with high and low control mixtures revealed signal intensity coefficients of variation of 3.0-27.5%. The Exactive-MS method was selective for the compounds of interest. Overall, concordance ranged from 89.1% to 100% for the screening of antiretroviral drugs in clinical plasma specimens as compared to LC-MS/MS methods.
Conclusion: Using the Exactive-MS, we developed and validated a highly selective, robust method for the multiplexed detection of 15 antiretroviral drugs.
Keywords: Antiretroviral; Clinical trials; Exactive-MS; High-resolution mass spectrometry; Validation.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Global report: UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic 2012. 2012 http://www.unaids.org/en/resources/publications/2012.
-
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA) FDA-approved ARV drugs, February 2013. 2013 http://www.fda.gov/ForConsumers/byAudience/ForPatientAdvocates/HIVandAID....
-
- Volberding PA, Deeks SG. Antiretroviral therapy and management of HIV infections. Lancet. 2010;376:49–62. - PubMed
-
- Sierra-Aragon S S, Walter H. Targets for inhibition of HIV replication: entry, enzyme action, release and maturation. Intervirology. 2012;55:84–97. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Antiretroviral therapy for HIV infection in adults and adolescents: Recommendations for a public health approach: 2010 revision. 20102010 http://www.who.int/hiv/pub/arv/adult2010/en/ - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

