Coinfection of human herpesviruses 6A (HHV-6A) and HHV-6B as demonstrated by novel digital droplet PCR assay
- PMID: 24663487
- PMCID: PMC3963908
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092328
Coinfection of human herpesviruses 6A (HHV-6A) and HHV-6B as demonstrated by novel digital droplet PCR assay
Abstract
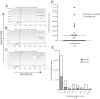
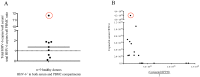
The human herpesviruses HHV-6A and HHV-6B have been associated with various neurologic disorders partly due to the detection of elevated viral DNA levels in patients compared to controls. However the reported frequency of these viruses varies widely, likely reflecting differences in PCR methodologies used for detection. Digital droplet PCR (ddPCR) is a third generation PCR technology that enables the absolute quantification of target DNA molecules. Mounting evidence of the biological differences between HHV-6A and HHV-6B has led to their recent reclassification as separate species. As it is now especially relevant to investigate each virus, our objectives were to first design a multiplex HHV-6A and HHV-6B ddPCR assay and then to investigate the incidence of HHV-6A and HHV-6B coinfection in samples from healthy donors and patients with MS, a disease in which HHV-6 is thought to play a role. In our assessment of healthy donors, we observed a heretofore-underappreciated high frequency of coinfection in PBMC and serum, and found that our assay precisely detects both HHV-6A and HHV-6B chromosomally integrated virus, which has important implications in clinical settings. Interestingly, upon comparing the saliva from MS patients and healthy donors, we detected a significantly elevated frequency of coinfection in MS saliva; increased detection of HHV-6A in MS patients is consistent with other studies suggesting that this viral species (thought to be more neurotropic than HHV-6B) is more prevalent among MS patients compared to healthy donors. As the biology and disease associations between these two viral species differ, identifying and quantifying both species of HHV-6 may provide clinically relevant information, as well as enhance our understanding of the roles of each in health and disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Using Droplet Digital PCR to Detect Coinfection of Human Herpesviruses 6A and 6B (HHV-6A and HHV-6B) in Clinical Samples.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1768:99-109. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7778-9_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29717439
-
Detection of Human Herpesvirus 6B (HHV-6B) Reactivation in Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipients with Inherited Chromosomally Integrated HHV-6A by Droplet Digital PCR.J Clin Microbiol. 2016 May;54(5):1223-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.03275-15. Epub 2016 Feb 17. J Clin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26888901 Free PMC article.
-
Coinfection With Human Herpesvirus (HHV)-6B in Immunocompetent, Healthy Individuals With Chromosomally Integrated HHV-6A.J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2021 Mar 26;10(2):175-178. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piaa009. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2021. PMID: 31972018
-
[Diagnosis and practice of virological monitoring of infections by the human herpesviruses 6A and 6B].Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 2016 Mar-Apr;74(2):156-67. doi: 10.1684/abc.2016.1122. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 2016. PMID: 27029721 Review. French.
-
Update on infections with human herpesviruses 6A, 6B, and 7.Med Mal Infect. 2017 Mar;47(2):83-91. doi: 10.1016/j.medmal.2016.09.004. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Med Mal Infect. 2017. PMID: 27773488 Review.
Cited by
-
Past, present, and future perspectives on the diagnosis of Roseolovirus infections.Curr Opin Virol. 2014 Dec;9:84-90. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2014.09.014. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Curr Opin Virol. 2014. PMID: 25462438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD8+ T Cells Prevent Lethality from Neonatal Murine Roseolovirus Infection.J Immunol. 2017 Nov 1;199(9):3212-3221. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700982. Epub 2017 Oct 2. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28972091 Free PMC article.
-
Viral infections and their relationship to neurological disorders.Arch Virol. 2021 Mar;166(3):733-753. doi: 10.1007/s00705-021-04959-6. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Arch Virol. 2021. PMID: 33502593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of salivary human herpesviruses in pediatric multiple sclerosis cases and controls.Mult Scler. 2019 Apr;25(5):644-652. doi: 10.1177/1352458518765654. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Mult Scler. 2019. PMID: 29569515 Free PMC article.
-
Variation in human herpesvirus 6B telomeric integration, excision, and transmission between tissues and individuals.Elife. 2021 Sep 21;10:e70452. doi: 10.7554/eLife.70452. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34545807 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ward KN (2005) The natural history and laboratory diagnosis of human herpesviruses-6 and -7 infections in the immunocompetent. J Clin Virol 32: 183–193. - PubMed
-
- De Bolle L, Van Loon J, De Clercq E, Naesens L (2005) Quantitative analysis of human herpesvirus 6 cell tropism. J Med Virol 75: 76–85. - PubMed
-
- (2012) Virus Taxonomy: Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. 1338 pages p.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

