A metabolomic perspective on coeliac disease
- PMID: 24665364
- PMCID: PMC3934717
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/756138
A metabolomic perspective on coeliac disease
Abstract
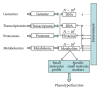
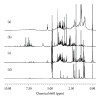
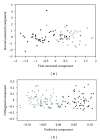
Metabolomics is an "omic" science that is now emerging with the purpose of elaborating a comprehensive analysis of the metabolome, which is the complete set of metabolites (i.e., small molecules intermediates) in an organism, tissue, cell, or biofluid. In the past decade, metabolomics has already proved to be useful for the characterization of several pathological conditions and offers promises as a clinical tool. A metabolomics investigation of coeliac disease (CD) revealed that a metabolic fingerprint for CD can be defined, which accounts for three different but complementary components: malabsorption, energy metabolism, and alterations in gut microflora and/or intestinal permeability. In this review, we will discuss the major advancements in metabolomics of CD, in particular with respect to the role of gut microbiome and energy metabolism.
Figures
References
-
- Murray JA, van Dyke C, Plevak MF, Dierkhising RA, Zinsmeister AR, Melton LJ., III Trends in the identification and clinical features of celiac disease in a North American community, 1950–2001. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2003;1(1):19–27. - PubMed
-
- Mäki M, Mustalahti K, Kokkonen J, et al. Prevalence of celiac disease among children in Finland. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2003;348(25):2517–2524. - PubMed
-
- Catassi C, Ratsch IM, Fabiani E, et al. High prevalence of undiagnosed coeliac disease in 5280 Italian students screened by antigliadin antibodies. Acta Paediatrica. 1995;84(6):672–676. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

