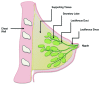
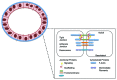
Ductal barriers in mammary epithelium
- PMID: 24665412
- PMCID: PMC3783220
- DOI: 10.4161/tisb.25933
Ductal barriers in mammary epithelium
Abstract
Tissue barriers play an integral role in the biology and pathobiology of mammary ductal epithelium. In normal breast physiology, tight and adherens junctions undergo dynamic changes in permeability in response to hormonal and other stimuli, while several of their proteins are directly involved in mammary tumorigenesis. This review describes first the structure of mammary ductal epithelial barriers and their role in normal mammary development, examining the cyclical changes in response to puberty, pregnancy, lactation and involution. It then examines the role of adherens and tight junctions and the participation of their constituent proteins in mammary tumorigenic functions such as migration, invasion and metastasis. Finally, it discusses the potential of these adhesion proteins as both prognostic biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets in breast cancer.
Keywords: adhesion; breast cancer; breast ductal epithelium; breast epithelial barrier; breast tumorigenesis; hormones; mammary epithelium; metastasis; tight junctions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Milk secretion and ejection are impaired in the mammary gland of mice harboring a Cx43 mutant while expression and localization of tight and adherens junction proteins remain unchanged.Biol Reprod. 2010 May;82(5):837-47. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.109.081406. Epub 2010 Jan 20. Biol Reprod. 2010. PMID: 20089884
-
Adhesion in mammary development: novel roles for E-cadherin in individual and collective cell migration.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015;112:353-82. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2014.12.001. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25733146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tight junction regulation in the mammary gland.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 1998 Jul;3(3):233-46. doi: 10.1023/a:1018707309361. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 1998. PMID: 10819511 Review.
-
Differential expression of claudin 1, 3, and 4 during normal mammary gland development in the mouse.DNA Cell Biol. 2006 Feb;25(2):79-86. doi: 10.1089/dna.2006.25.79. DNA Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16460231
-
Connexins, E-cadherin, Claudin-7 and β-catenin transiently form junctional nexuses during the post-natal mammary gland development.Dev Biol. 2016 Aug 1;416(1):52-68. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.06.011. Epub 2016 Jun 9. Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27291930
Cited by
-
Dynamic aberrant NF-κB spurs tumorigenesis: a new model encompassing the microenvironment.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015 Aug;26(4):389-403. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2015.06.001. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015. PMID: 26119834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental selection during the last ice age on the mother-to-infant transmission of vitamin D and fatty acids through breast milk.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 May 8;115(19):E4426-E4432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1711788115. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29686092 Free PMC article.
-
Biological underpinnings of breastfeeding challenges: the role of genetics, diet, and environment on lactation physiology.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Aug 1;311(2):E405-22. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00495.2015. Epub 2016 Jun 28. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 27354238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactational Amenorrhea: Neuroendocrine Pathways Controlling Fertility and Bone Turnover.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 31;23(3):1633. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031633. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A genetic variant in SLC30A2 causes breast dysfunction during lactation by inducing ER stress, oxidative stress and epithelial barrier defects.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 23;8(1):3542. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21505-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29476070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin H, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin D. GLOBOCAN 2008 v1.2, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 10 [Internet]. 2010 [cited; Available from: http://globocan.iarc.fr
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources