Human cathelicidin LL-37 and its derivative IG-19 regulate interleukin-32-induced inflammation
- PMID: 24666281
- PMCID: PMC4137957
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.12291
Human cathelicidin LL-37 and its derivative IG-19 regulate interleukin-32-induced inflammation
Abstract
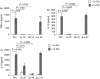
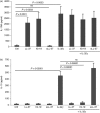
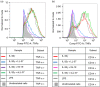
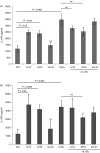
Human cathelicidin LL-37 protects against infections and endotoxin-induced inflammation. In a recent study we have shown that IG-19, an LL-37-derived peptide, protects in a murine model of arthritis. Cytokine interleukin-32 (IL-32) is elevated and directly associated with the disease severity of inflammatory arthritis. Therefore, in this study we examined the effects of LL-37 and IG-19 on IL-32-induced responses in human peripheral blood-derived mononuclear cells (PBMC) and macrophages. We showed that CD14(+) monocytes are the primary cells that produce pro-inflammatory tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) following stimulation of PBMC with IL-32. We demonstrated that LL-37 and IG-19 significantly suppress IL-32-induced production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, e.g. TNF-α and IL-1β, without altering chemokine production. In contrast, LL-37 and IG-19 enhance the production of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-1RA. Further mechanistic studies revealed that LL-37 and IG-19 suppress IL-32-mediated phosphorylation of Fyn (Y420) Src kinase. In contrast, IL-32-mediated phosphorylation of AKT-1 (T308) and MKP-1 (S359) is not suppressed by the peptides. LL-37 and IG-19 alone induce the phosphorylation of MKP-1 (S359), which is a known negative regulator of inflammation. Furthermore, the peptides induce the activity of p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase, which is known to phosphorylate MKP-1 (S359). This is the first study to demonstrate the regulation of IL-32-induced inflammation by LL-37 and its derivative peptide IG-19. The mechanistic results from this study suggest that regulation of immune-mediated inflammation by these peptides may be controlled by the dual phosphatase MKP-1. We speculate that LL-37 and its derivatives may contribute to the control of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: LL-37; cathelicidin; host defence peptides; inflammation; interleukin-32.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Host Defense Peptide LL-37-Mediated Chemoattractant Properties, but Not Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine IL-1RA Production, Is Selectively Controlled by Cdc42 Rho GTPase via G Protein-Coupled Receptors and JNK Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase.Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 13;9:1871. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01871. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30158931 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory Functions of the Human Cathelicidin LL-37 (aa 13-31)-Derived Peptides are Associated with Predicted α-Helical Propensity and Hydrophobic Index.Biomolecules. 2019 Sep 18;9(9):501. doi: 10.3390/biom9090501. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31540479 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of interleukin-1β-induced inflammatory responses by a synthetic cationic innate defence regulator peptide, IDR-1002, in synovial fibroblasts.Arthritis Res Ther. 2011 Aug 11;13(4):R129. doi: 10.1186/ar3440. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011. PMID: 21835002 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Cathelicidin Peptide LL-37, an Antimicrobial Agent, in a Murine Sepsis Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 19;21(17):5973. doi: 10.3390/ijms21175973. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32825174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The human cathelicidin LL-37: a multifunctional peptide involved in infection and inflammation in the lung.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2005;18(5):321-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2005.01.001. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15939310 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-32θ gene expression in acute myeloid leukemia suppresses TNF-α production.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 1;6(38):40747-61. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5688. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26516703 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated serum levels of cathelicidin and β-defensin 2 are associated with basal cell carcinoma.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2021;46(3):360-364. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2021.109707. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34764808 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic Hybrids: the Next Generation of Agents and Adjuvants against Gram-Negative Pathogens?Clin Microbiol Rev. 2018 Mar 14;31(2):e00077-17. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00077-17. Print 2018 Apr. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29540434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the Roles of Host Defense Peptides in Immune Modulation: From Antimicrobial Action to Potential as Adjuvants.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Mar 28;33(3):288-298. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2301.01005. Epub 2023 Feb 10. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36775853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokines and microbicidal molecules regulated by IL-32 in THP-1-derived human macrophages infected with New World Leishmania species.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017 Feb 27;11(2):e0005413. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005413. eCollection 2017 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017. PMID: 28241012 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rajanbabu V, Chen JY. Antiviral function of tilapia hepcidin 1-5 and its modulation of immune-related gene expressions against infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV) in Chinook salmon embryo (CHSE)-214 cells. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011;30:39–44. - PubMed
-
- Kindrachuk J, Scruten E, Attah-Poku S, Bell K, Potter A, Babiuk LA, Griebel PJ, Napper S. Stability, toxicity and biological activity of host defense peptide BMAP28 and its inversed and retro-inversed isomers. Biopolymers. 2011;96:14–24. - PubMed
-
- Bowdish DM, Davidson DJ, Lau YE, Lee K, Scott MG, Hancock RE. Impact of LL-37 on anti-infective immunity. J Leukoc Biol. 2005;77:451–9. - PubMed
-
- Arnett E, Lehrer RI, Pratikhya P, Lu W, Seveau S. Defensins enable macrophages to inhibit the intracellular proliferation of Listeria monocytogenes. Cell Microbiol. 2011;13:635–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

