Amelioration of adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity by Salsola kali aqueous extract is mediated by lowering oxidative stress
- PMID: 24666516
- PMCID: PMC6837571
- DOI: 10.1179/1351000214Y.0000000088
Amelioration of adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity by Salsola kali aqueous extract is mediated by lowering oxidative stress
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the cardioprotective effect of the Salsola kali aqueous extract against adriamycin (ADR)-induced cardiotoxicity in male Swiss albino mice.
Methods: The aqueous extract of S. kali was phytochemically screened by traditional methods for different classes and further evaluated for antioxidant activity in vitro. In vivo, cardioprotective evaluation of the extract was designed to have four groups of mice: (1) control group (distilled water, orally; normal saline, intraperitoneally (i.p.)); (2) ADR group (15 mg/kg, i.p.); (3) aqueous S. kali extract (200 mg/kg, orally); and (4) ADR + S. kali group. ADR (5 mg/kg) was injected three times over 2 weeks while S. kali was orally administered daily for 3 weeks (1 week before and 2 weeks during ADR treatment). Cardioprotective properties were assessed using biochemical and histopathological approaches.
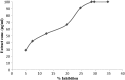
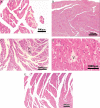
Results: ADR caused a significant increase in serum enzymes (lactate dehydrogenase, creatine phosphokinase, aspartate aminotransferase, and alanine aminotransferase). Myocardial levels of malondialdehyde, nitric oxide, and reduced glutathione, as well as the activities of superoxide dismutase and catalase increased while the activities of glutathione peroxidase and glutathione S-transferase declined. Histopathological examination of heart sections revealed that ADR caused myofibrils loss, necrosis and cytoplasmic vacuolization.
Discussion: Pretreatment with S. kali aqueous extract normalized serum and antioxidant enzymes minimized lipid peroxidation and cardiac damage. These results have suggested that the extract has antioxidant activity, indicating that the mechanism of cardioprotection during ADR treatment is mediated by lowering oxidative stress.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Cardiotoxicity; Chenopodiaceae; Free radicals; Histopathology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective effect of Piper longum L. on oxidative stress induced injury and cellular abnormality in adriamycin induced cardiotoxicity in rats.Indian J Exp Biol. 2008 Jul;46(7):528-33. Indian J Exp Biol. 2008. PMID: 18807757
-
Trigonella stellata reduced the deleterious effects of diabetes mellitus through alleviation of oxidative stress, antioxidant- and drug-metabolizing enzymes activities.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Jun 28;256:112821. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112821. Epub 2020 Apr 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32251758
-
Effect of fenugreek seed extract on adriamycin-induced hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress in albino rats.Toxicol Ind Health. 2012 Nov;28(10):876-85. doi: 10.1177/0748233711425076. Epub 2011 Nov 14. Toxicol Ind Health. 2012. PMID: 22082829
-
Chemoprotective effect of Vernonia amygdalina Del. (Astereacea) against 2-acetylaminofluorene-induced hepatotoxicity in rats.Toxicol Ind Health. 2016 Jan;32(1):47-58. doi: 10.1177/0748233713498436. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Toxicol Ind Health. 2016. PMID: 24021430
-
Alcohol stress on cardiac tissue - ameliorative effects of Thespesia populnea leaf extract.J Cardiol. 2014 Jun;63(6):449-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2013.10.015. Epub 2013 Dec 2. J Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24296114
Cited by
-
Amelioration of aluminum-induced hepatic and nephrotoxicity by Premna odorata extract is mediated by lowering MMP9 and TGF-β gene alterations in Wistar rat.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Oct;29(48):72827-72838. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-20735-8. Epub 2022 May 26. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35614356 Free PMC article.
-
The old world salsola as a source of valuable secondary metabolites endowed with diverse pharmacological activities: a review.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):2036-2062. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2102005. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35875938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genus Salsola: Chemistry, Biological Activities and Future Prospective-A Review.Plants (Basel). 2022 Mar 8;11(6):714. doi: 10.3390/plants11060714. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35336596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytochemical profiling of Salsola tetragona Delile by LC-HR/MS and investigation of the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, cytotoxic, antibacterial and anti-SARS-CoV-2 activities.Saudi Pharm J. 2023 Sep;31(9):101731. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.101731. Epub 2023 Aug 5. Saudi Pharm J. 2023. PMID: 37638223 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Minotti G, Menna P, Salvatorelli E, Cairo G, Gianni L. Anthracyclines: molecular advances and pharmacologic developments in antitumor activity and cardiotoxicity. Pharmacol Rev 2004;56(2):185–229. - PubMed
-
- Kim DS, Kim HR, Woo ER, Hong ST, Chae HJ, Chae SW. Inhibitory effects of rosmarinic acid on adriamycin-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiac muscle cells by inhibiting reactive oxygen species and the activations of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Biochem Pharmacol 2005;70(7):1066–78. - PubMed
-
- Menna P, Salvatorelli E, Minotti G. Cardiotoxicity of antitumor drugs. Chem Res Toxicol 2008;21(5):978–89. - PubMed
-
- Yilmaz S, Atessahin A, Sahna E, Karahan I, Ozer S. Protective effect of lycopene on adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Toxicology 2006;218:164–71. - PubMed
-
- Doroshow JH. Doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity. N Engl J Med 1991;324(12):843–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
