Genome-wide association study for intramuscular fat deposition and composition in Nellore cattle
- PMID: 24666668
- PMCID: PMC4230646
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2156-15-39
Genome-wide association study for intramuscular fat deposition and composition in Nellore cattle
Abstract
Background: Meat from Bos taurus and Bos indicus breeds are an important source of nutrients for humans and intramuscular fat (IMF) influences its flavor, nutritional value and impacts human health. Human consumption of fat that contains high levels of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) can reduce the concentration of undesirable cholesterol (LDL) in circulating blood. Different feeding practices and genetic variation within and between breeds influences the amount of IMF and fatty acid (FA) composition in meat. However, it is difficult and costly to determine fatty acid composition, which has precluded beef cattle breeding programs from selecting for a healthier fatty acid profile. In this study, we employed a high-density single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) chip to genotype 386 Nellore steers, a Bos indicus breed and, a Bayesian approach to identify genomic regions and putative candidate genes that could be involved with deposition and composition of IMF.
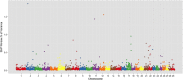
Results: Twenty-three genomic regions (1-Mb SNP windows) associated with IMF deposition and FA composition that each explain ≥1% of the genetic variance were identified on chromosomes 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 17, 26 and 27. Many of these regions were not previously detected in other breeds. The genes present in these regions were identified and some can help explain the genetic basis of deposition and composition of fat in cattle.
Conclusions: The genomic regions and genes identified contribute to a better understanding of the genetic control of fatty acid deposition and can lead to DNA-based selection strategies to improve meat quality for human consumption.
Figures


References
-
- Laborde FL, Mandell IB, Tosh JJ, Wilton JW, Buchanan-Smith JG. Breed effects on growth performance, carcass characteristics, fatty acid composition, and palatability attributes in finishing steers. J Anim Sci. 2001;79(2):355–365. - PubMed
-
- Rule DC, MacNeil MD, Short RE. Influence of sire growth potential, time on feed, and growing-finishing strategy on cholesterol and fatty acids of the ground carcass and longissimus muscle of beef steers. J Anim Sci. 1997;75(6):1525–1533. - PubMed
-
- Matukumalli LK, Lawley CT, Schnabel RD, Taylor JF, Allan MF, Heaton MP, O’Connell J, Moore SS, Smith TP, Sonstegard TS, Van Tassel CP. Development and characterization of a high density SNP genotyping assay for cattle. PLoS One. 2009;4(4):e5350. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005350. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

