Carboxymethyl chitosan-folic acid-conjugated Fe3O4@SiO2 as a safe and targeting antitumor nanovehicle in vitro
- PMID: 24667013
- PMCID: PMC4229976
- DOI: 10.1186/1556-276X-9-146
Carboxymethyl chitosan-folic acid-conjugated Fe3O4@SiO2 as a safe and targeting antitumor nanovehicle in vitro
Abstract
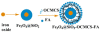
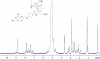
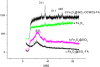
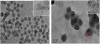
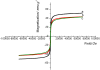
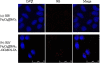
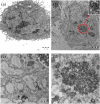
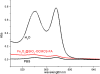
A synthetic method to prepare a core-shell-structured Fe3O4@SiO2 as a safe nanovehicle for tumor cell targeting has been developed. Superparamagnetic iron oxide is encapsulated inside nonporous silica as the core to provide magnetic targeting. Carboxymethyl chitosan-folic acid (OCMCS-FA) synthesized through coupling folic acid (FA) with OCMCS is then covalently linked to the silica shell and renders new and improved functions because of the original biocompatible properties of OCMCS and the targeting efficacy of FA. Cellular uptake of the nanovehicle was assayed by confocal laser scanning microscope using rhodamine B (RB) as a fluorescent marker in HeLa cells. The results show that the surface modification of the core-shell silica nanovehicle with OCMCS-FA enhances the internalization of nanovehicle to HeLa cells which over-express the folate receptor. The cell viability assay demonstrated that Fe3O4@SiO2-OCMCS-FA nanovehicle has low toxicity and can be used as an eligible candidate for drug delivery system. These unique advantages make the prepared core-shell nanovehicle promising for cancer-specific targeting and therapy.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Folate-conjugated Fe3O4@SiO2@gold nanorods@mesoporous SiO2 hybrid nanomaterial: a theranostic agent for magnetic resonance imaging and photothermal therapy.J Mater Chem B. 2013 Jun 21;1(23):2934-2942. doi: 10.1039/c3tb20090f. Epub 2013 May 10. J Mater Chem B. 2013. PMID: 32260860
-
Inorganic nanovehicle for potential targeted drug delivery to tumor cells, tumor optical imaging.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015 Mar 11;7(9):5089-96. doi: 10.1021/am507345j. Epub 2015 Mar 2. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015. PMID: 25693506
-
Tumor selectivity of stealth multi-functionalized superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles.Int J Pharm. 2011 Feb 14;404(1-2):180-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.10.038. Epub 2010 Nov 16. Int J Pharm. 2011. PMID: 21087660
-
Multi-functional core-shell Fe3O4@Au nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis and therapy.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019 Feb 1;174:252-259. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.11.004. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019. PMID: 30469046
-
pH sensitive core-shell magnetic nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery in cancer therapy.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2016;57(1):23-32. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2016. PMID: 27151685 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus using magnetic nanobead-based immunoseparation and quantum dot-based immunofluorescence.RSC Adv. 2021 Dec 1;11(61):38638-38647. doi: 10.1039/d1ra07580b. eCollection 2021 Nov 29. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35493221 Free PMC article.
-
Release of Doxorubicin by a Folate-Grafted, Chitosan-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticle.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017 Apr 13;7(4):85. doi: 10.3390/nano7040085. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28406429 Free PMC article.
-
Advances with metal oxide-based nanoparticles as MDR metastatic breast cancer therapeutics and diagnostics.RSC Adv. 2022 Nov 17;12(51):32956-32978. doi: 10.1039/d2ra02005j. eCollection 2022 Nov 15. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36425155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Folic Acid-Chitosan Oligosaccharide Conjugates Decorated Nanodiamond as Potential Carriers for the Oral Delivery of Doxorubicin.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023 Mar 25;24(4):86. doi: 10.1208/s12249-023-02545-4. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023. PMID: 36964428
References
-
- Lee JH, Lee K, Moon SH, Lee YH, Park TG, Cheon J. All-in-one target-cell-specific magnetic nanoparticles for simultaneous molecular imaging and siRNA delivery. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2009;4:4174–4179. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

