MUC1: a multifaceted oncoprotein with a key role in cancer progression
- PMID: 24667139
- PMCID: PMC5500204
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2014.02.007
MUC1: a multifaceted oncoprotein with a key role in cancer progression
Abstract
The transmembrane glycoprotein Mucin 1 (MUC1) is aberrantly glycosylated and overexpressed in a variety of epithelial cancers, and plays a crucial role in progression of the disease. Tumor-associated MUC1 differs from the MUC1 expressed in normal cells with regard to its biochemical features, cellular distribution, and function. In cancer cells, MUC1 participates in intracellular signal transduction pathways and regulates the expression of its target genes at both the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. This review highlights the structural and functional differences that exist between normal and tumor-associated MUC1. We also discuss the recent advances made in the use of MUC1 as a biomarker and therapeutic target for cancer.
Keywords: ABC pumps; EMT; Mucin 1 (MUC1); VNTR; cancer; cancer stem cell.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


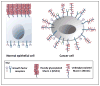
References
-
- Hattrup CL, Gendler SJ. Structure and function of the cell surface (tethered) mucins. Annu Rev Physiol. 2008;70:431–457. - PubMed
-
- Gendler SJ, Spicer AP. Epithelial mucin genes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:607–634. - PubMed
-
- Gendler SJ. MUC1, the renaissance molecule. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2001;6:339–353. - PubMed
-
- Chang JF, et al. The epithelial mucin, MUC1, is expressed on resting T lymphocytes and can function as a negative regulator of T cell activation. Cell Immunol. 2000;201:83–88. - PubMed
-
- Hanisch FG, Müller S. MUC1: the polymorphic appearance of a human mucin. Glycobiology. 2000;10:439–449. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

