JMJD6 promotes colon carcinogenesis through negative regulation of p53 by hydroxylation
- PMID: 24667498
- PMCID: PMC3965384
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001819
JMJD6 promotes colon carcinogenesis through negative regulation of p53 by hydroxylation
Abstract
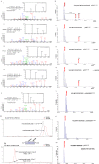
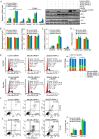
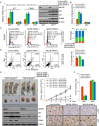
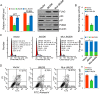
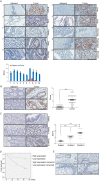
Jumonji domain-containing 6 (JMJD6) is a member of the Jumonji C domain-containing family of proteins. Compared to other members of the family, the cellular activity of JMJD6 is still not clearly defined and its biological function is still largely unexplored. Here we report that JMJD6 is physically associated with the tumor suppressor p53. We demonstrated that JMJD6 acts as an α-ketoglutarate- and Fe(II)-dependent lysyl hydroxylase to catalyze p53 hydroxylation. We found that p53 indeed exists as a hydroxylated protein in vivo and that the hydroxylation occurs mainly on lysine 382 of p53. We showed that JMJD6 antagonizes p53 acetylation, promotes the association of p53 with its negative regulator MDMX, and represses transcriptional activity of p53. Depletion of JMJD6 enhances p53 transcriptional activity, arrests cells in the G1 phase, promotes cell apoptosis, and sensitizes cells to DNA damaging agent-induced cell death. Importantly, knockdown of JMJD6 represses p53-dependent colon cell proliferation and tumorigenesis in vivo, and significantly, the expression of JMJD6 is markedly up-regulated in various types of human cancer especially in colon cancer, and high nuclear JMJD6 protein is strongly correlated with aggressive clinical behaviors of colon adenocarcinomas. Our results reveal a novel posttranslational modification for p53 and support the pursuit of JMJD6 as a potential biomarker for colon cancer aggressiveness and a potential target for colon cancer intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Fadok VA, Bratton DL, Rose DM, Pearson A, Ezekewitz RA, et al. (2000) A receptor for phosphatidylserine-specific clearance of apoptotic cells. Nature 405: 85–90. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Wu YC, Fadok VA, Lee MC, Gengyo-Ando K, et al. (2003) Cell corpse engulfment mediated by C. elegans phosphatidylserine receptor through CED-5 and CED-12. Science 302: 1563–1566. - PubMed
-
- Hong JR, Lin GH, Lin CJ, Wang WP, Lee CC, et al. (2004) Phosphatidylserine receptor is required for the engulfment of dead apoptotic cells and for normal embryonic development in zebrafish. Development 131: 5417–5427. - PubMed
-
- Chang B, Chen Y, Zhao Y, Bruick RK (2007) JMJD6 is a histone arginine demethylase. Science 318: 444–447. - PubMed
-
- Webby CJ, Wolf A, Gromak N, Dreger M, Kramer H, et al. (2009) Jmjd6 catalyses lysyl-hydroxylation of U2AF65, a protein associated with RNA splicing. Science 325: 90–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

