Z-disc-associated, alternatively spliced, PDZ motif-containing protein (ZASP) mutations in the actin-binding domain cause disruption of skeletal muscle actin filaments in myofibrillar myopathy
- PMID: 24668811
- PMCID: PMC4036366
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.550418
Z-disc-associated, alternatively spliced, PDZ motif-containing protein (ZASP) mutations in the actin-binding domain cause disruption of skeletal muscle actin filaments in myofibrillar myopathy
Abstract
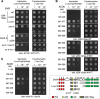
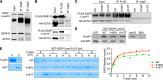
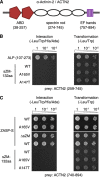
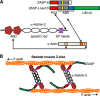
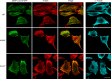
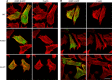
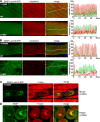
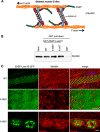
The core of skeletal muscle Z-discs consists of actin filaments from adjacent sarcomeres that are cross-linked by α-actinin homodimers. Z-disc-associated, alternatively spliced, PDZ motif-containing protein (ZASP)/Cypher interacts with α-actinin, myotilin, and other Z-disc proteins via the PDZ domain. However, these interactions are not sufficient to maintain the Z-disc structure. We show that ZASP directly interacts with skeletal actin filaments. The actin-binding domain is between the modular PDZ and LIM domains. This ZASP region is alternatively spliced so that each isoform has unique actin-binding domains. All ZASP isoforms contain the exon 6-encoded ZASP-like motif that is mutated in zaspopathy, a myofibrillar myopathy (MFM), whereas the exon 8-11 junction-encoded peptide is exclusive to the postnatal long ZASP isoform (ZASP-LΔex10). MFM is characterized by disruption of skeletal muscle Z-discs and accumulation of myofibrillar degradation products. Wild-type and mutant ZASP interact with α-actin, α-actinin, and myotilin. Expression of mutant, but not wild-type, ZASP leads to Z-disc disruption and F-actin accumulation in mouse skeletal muscle, as in MFM. Mutations in the actin-binding domain of ZASP-LΔex10, but not other isoforms, cause disruption of the actin cytoskeleton in muscle cells. These isoform-specific mutation effects highlight the essential role of the ZASP-LΔex10 isoform in F-actin organization. Our results show that MFM-associated ZASP mutations in the actin-binding domain have deleterious effects on the core structure of the Z-discs in skeletal muscle.
Keywords: Actin; Actinin; Muscular Dystrophy; Myofibrillar Myopathy; Myotilin; Protein Complex; Protein-Protein Interaction; Skeletal Muscle; Z-disc; ZASP.
Figures
References
-
- Luther P. K. (2000) Three-dimensional structure of a vertebrate muscle Z-band: implications for titin and α-actinin binding. J. Struct. Biol. 129, 1–16 - PubMed
-
- Sanger J. M., Sanger J. W. (2008) The dynamic Z bands of striated muscle cells. Sci. Signal. 1, pe37. - PubMed
-
- Frank D., Kuhn C., Katus H. A., Frey N. (2006) The sarcomeric Z-disc: a nodal point in signalling and disease. J. Mol. Med. 84, 446–468 - PubMed
-
- Nakano S., Engel A. G., Waclawik A. J., Emslie-Smith A. M., Busis N. A. (1996) Myofibrillar myopathy with abnormal foci of desmin positivity: I: light and electron microscopy analysis of 10 cases. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 55, 549–562 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

