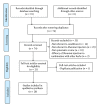
An overview of systematic reviews of shenmai injection for healthcare
- PMID: 24669229
- PMCID: PMC3942339
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/840650
An overview of systematic reviews of shenmai injection for healthcare
Abstract
Shenmai injection (SMI) is widely applied in clinical practice as an organ protector. This overview is to evaluate the current evidence from systematic reviews (SRs) of SMI for healthcare. The literature searches were carried out in 6 databases without language restrictions until December 2012. The quality of the primary studies from the respective SRs was evaluated by using Jadad score. The overview quality assessment questionnaire (OQAQ) was used to evaluate the methodological quality of all included SRs. Twenty eligible SRs were identified. They reported a wide range of conditions, including SMI for cardio/cerebrovascular diseases, viral myocarditis, tumor chemotherapy, and adverse drug reactions. Most of the primary studies were of good quality only in 1 SR of non-small-cell lung cancer. According to the OQAQ scores, the quality of included SRs was variable and six reviews were of high quality with a score of 5 points. Two SRs showed that SMI had low adverse drug reaction occurrence. In conclusion, there is mixed evidence to support efficacy of SMI for an adjunct therapy to tumor chemotherapy and premature evidence for the use of SMI for cardio/cerebrovascular disorders and viral myocarditis. SMI seems generally safe for clinical application. Further large sample-size and well-designed RCTs are needed.
Similar articles
-
[Overview of systematic reviews on Shenmai Injection in prevention and treatment of diseases].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Aug;46(15):3998-4007. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210113.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34472277 Review. Chinese.
-
The clinical efficacy of curcumin-containing nutraceuticals: An overview of systematic reviews.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Aug;134:79-91. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.06.007. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 29890252 Review.
-
An Overview of Systematic Reviews of Danhong Injection for Ischemic Stroke.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:8949835. doi: 10.1155/2016/8949835. Epub 2016 Jul 31. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 27547231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Overview of systematic reviews of Qingkailing Injection].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Jul;46(13):3446-3454. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210407.502. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34396765 Chinese.
-
Benefits and Safety of Chinese Herbal Medicine in Treating Psoriasis: An Overview of Systematic Reviews.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 1;12:680172. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.680172. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34276371 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ginsenoside Rb1 and Rd Remarkably Inhibited the Hepatic Uptake of Ophiopogonin D in Shenmai Injection Mediated by OATPs/oatps.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Aug 22;9:957. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00957. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30186179 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of Ginseng-Ophiopogon Injection on Enhancing Physical Function by Pharmacogenomics and Metabolomics Evaluation.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(19):2838-2849. doi: 10.2174/0113862073244102231020050502. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 37957852
-
The Inhibition Effects of Shenmai Injection on Acetylcholine-Induced Catecholamine Synthesis and Secretion by Modulating Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Ion Channels in Cultured Bovine Adrenal Medullary Cells.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Dec 15;2020:8514926. doi: 10.1155/2020/8514926. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 33456492 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Shenmai Injection on the Pharmacokinetics of Dasatinib: An In-Depth In vivo Analysis Utilizing UPLC-MS/MS Technique.Curr Drug Metab. 2024;25(9):670-676. doi: 10.2174/0113892002336775250108112738. Curr Drug Metab. 2024. PMID: 39901553
-
Shenmai-Yin decreased the clearance of nifedipine in rats: The involvement of time-dependent inhibition of nifedipine oxidation.J Food Drug Anal. 2019 Jan;27(1):284-294. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2018.10.005. Epub 2018 Nov 8. J Food Drug Anal. 2019. PMID: 30648582 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Qin CY. Zhengyin Maizhi (Pattern, Cause, Pulse, and Treatment) Beijing, China: Ancient Books of TCM; 2000.
-
- Xia C-H, Sun J-G, Wang G-J, et al. Herb-drug interactions: in vivo and in vitro effect of shenmai injection, a herbal preparation, on the Metabolic activities of hepatic cytochrome P450 3A1/2, 2C6, 1A2, and 2E1 in rats. Planta Medica. 2010;76(3):245–250. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Wang W, Zhao X, et al. Effect of Shenmai injection, a traditional Chinese medicine, on pulmonary dysfunction after tourniquet-induced limb ischemia-reperfusion. Journal of Trauma. 2011;71(4):893–897. - PubMed
-
- Zhao L-M, Ma L-J, Zhang L-X, Wu J-Z. Shenmai injection inhibiting the extracellular signal regulated kinase-induced human airway smooth muscle proliferation in asthma. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine. 2010;16(4):331–336. - PubMed
-
- Xia C, Wang G, Sun J, et al. Simultaneous determination of ginsenoside Rg1, Re, Rd, Rb1 and ophiopogonin D in rat plasma by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometric method and its application to pharmacokinetic study of ‘SHENMAI’ injection. Journal of Chromatography B. 2008;862(1-2):72–78. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials