Chinese medicinal formula Guanxin Shutong capsule protects the heart against oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by ischemic myocardial injury in rats
- PMID: 24669273
- PMCID: PMC3965158
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2014.1540
Chinese medicinal formula Guanxin Shutong capsule protects the heart against oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by ischemic myocardial injury in rats
Abstract
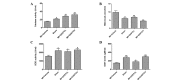
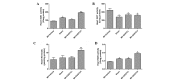
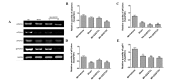
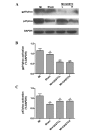
Guanxin Shutong capsule (GXSTC) is a Chinese medicinal formula that has been used clinically for the treatment of chest pain, depression, palpitation and cardiovascular diseases in China for almost 10 years. The aim of the present study was to investigate the protective mechanisms against oxidative stress and apoptosis that GXSTC exhibits in the hearts of rats with myocardial ischemia (MI). Infarct size and the levels of marker enzymes, including serum creatine kinase-isoenzyme (CK-MB), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and glutamate oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT), as well as the levels of nitric oxide (NO) and NO synthase (NOS) in the heart were measured by biochemical analysis assays. Levels of the antioxidants superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CATA), and glutathione (GSH), and the oxidative stress marker malondialdehyde (MDA), were also determined. Following a 6-week period of ischemia, myocardial apoptosis, as well as the protein and mRNA expression of NADPH oxidase, was evaluated. Myocardial NADPH oxidase activity was measured by protein expression of p47phox and gp91phox using western blot analysis and mRNA expression of p22phox, p47phox, p67phox and gp91phox using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. The results showed that daily oral treatment of the rats with GXSTC reduced infarct size, myocardial apoptosis, the levels of serum MDA, LDH, CK-MB and GOT and heart GOT, and increased the activities of total SOD, CATA, NOS and the levels of NO and GSH compared with those in vehicle-treated MI model rats. Administration of GXSTC for 6 weeks also reduced the mRNA expression of the NADPH oxidase subunits p47phox and gp91phox protein, as well as the expression of Bax and caspase-3 proteins. By contrast, Bcl-2 protein expression increased. In conclusion, the results demonstrate that GXSTC attenuates myocardial injury via antioxidative and antiapoptotic effects.
Keywords: Guanxin Shutong capsule; NADPH oxidase; myocardial infarction; oxidative stress.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Study of the Mechanism of Action of Guanxin Shutong Capsules in the Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease Based on Metabolomics.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 25;12:650438. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.650438. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33867992 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of Guanxin Shutong capsule drug-containing serum on tumor necrosis factor-α-induced endothelial dysfunction through nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase and the nitric oxide pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2014 Sep;8(3):998-1004. doi: 10.3892/etm.2014.1795. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Exp Ther Med. 2014. PMID: 25120637 Free PMC article.
-
Four Main Active Ingredients Derived from a Traditional Chinese Medicine Guanxin Shutong Capsule Cause Cardioprotection during Myocardial Ischemia Injury Calcium Overload Suppression.Phytother Res. 2017 Mar;31(3):507-515. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5787. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Phytother Res. 2017. PMID: 28164397
-
Kudiezi injection mitigates myocardial injury induced by acute cerebral ischemia in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Jan 5;17(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1514-1. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28056927 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the Multi-Target Mechanism of Guanxin-Shutong Capsule in Cerebrovascular Diseases: A Systems Pharmacology and Experimental Assessment.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 13;12:650770. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.650770. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34054530 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Guanxinshutong Alleviates Atherosclerosis by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Proinflammation in ApoE-/- Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Sep 16;2020:1219371. doi: 10.1155/2020/1219371. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 33014098 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic Comparison of Nine Bioactive Compounds of Guanxinshutong Capsule in Normal and Acute Myocardial Infarction Rats.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2022 Sep;47(5):653-665. doi: 10.1007/s13318-022-00777-6. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2022. PMID: 35751765
-
Kolaviron, a biflavonoid of Garcinia kola seed mitigates ischemic/reperfusion injury by modulation of pro-survival and apoptotic signaling pathways.J Intercult Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Sep 28;6(1):42-49. doi: 10.5455/jice.20160923100223. eCollection 2017 Jan-Mar. J Intercult Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 28163959 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the Mechanism of Action of Guanxin Shutong Capsules in the Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease Based on Metabolomics.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 25;12:650438. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.650438. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33867992 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Guanxin V in animal model of acute myocardial infarction.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Feb 22;21(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03211-7. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021. PMID: 33618704 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marzilli M, Affinito S, Focardi M. Changing scenario in chronic ischemic heart disease: therapeutic implications. Am J Cardiol. 2006;98:3J–7J. - PubMed
-
- Razavi HM, Hamilton JA, Feng Q. Modulation of apoptosis by nitric oxide: implications in myocardial ischemia and heart failure. Pharmacol Ther. 2005;106:147–162. - PubMed
-
- Kumar D, Lou H, Singal PK. Oxidative stress and apoptosis in heart dysfunction. Herz. 2002;27:662–668. - PubMed
-
- Qin F, Simeone M, Patel R. Inhibition of NADPH oxidase reduces myocardial oxidative stress and apoptosis and improves cardiac function in heart failure after myocardial infarction. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007;43:271–281. - PubMed
-
- Qin F, Liu YX, Zhao HW, Huang X, Ren P, Zhu ZY. Chinese medicinal formula Guan-Xin-Er-Hao protects the heart against oxidative stress induced by acute ischemic myocardial injury in rats. Phytomedicine. 2009;16:215–221. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
