The macrophage LBP gene is an LXR target that promotes macrophage survival and atherosclerosis
- PMID: 24671012
- PMCID: PMC4031943
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M047548
The macrophage LBP gene is an LXR target that promotes macrophage survival and atherosclerosis
Abstract
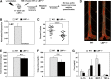
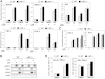
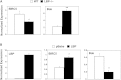
The liver X receptors (LXRs) are members of the nuclear receptor superfamily that regulate sterol metabolism and inflammation. We sought to identify previously unknown genes regulated by LXRs in macrophages and to determine their contribution to atherogenesis. Here we characterize a novel LXR target gene, the lipopolysaccharide binding protein (LBP) gene. Surprisingly, the ability of LXRs to control LBP expression is cell-type specific, occurring in macrophages but not liver. Treatment of macrophages with oxysterols or loading with modified LDL induces LBP in an LXR-dependent manner, suggesting a potential role for LBP in the cellular response to cholesterol overload. To investigate this further, we performed bone marrow transplant studies. After 18 weeks of Western diet feeding, atherosclerotic lesion burden was assessed revealing markedly smaller lesions in the LBP(-/-) recipients. Furthermore, loss of bone marrow LBP expression increased apoptosis in atherosclerotic lesions as determined by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling staining. Supporting in vitro studies with isolated macrophages showed that LBP expression does not affect cholesterol efflux but promotes the survival of macrophages in the setting of cholesterol loading. The LBP gene is a macrophage-specific LXR target that promotes foam cell survival and atherogenesis.
Keywords: atherogenesis; lipopolysaccharide binding protein; liver X receptor; nuclear receptor.
Figures





References
-
- Weber C., Noels H. 2011. Atherosclerosis: current pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Nat. Med. 17: 1410–1422. - PubMed
-
- Zadelaar S., Kleemann R., Verschuren L., de Vries-Van der Weij J., van der Hoorn J., Princen H. M., Kooistra T. 2007. Mouse models for atherosclerosis and pharmaceutical modifiers. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 27: 1706–1721. - PubMed
-
- Hansson G. K. 2005. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 352: 1685–1695. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

