Hierarchical functional specificity of cytosolic heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) nucleotide exchange factors in yeast
- PMID: 24671421
- PMCID: PMC4036327
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.530014
Hierarchical functional specificity of cytosolic heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) nucleotide exchange factors in yeast
Abstract
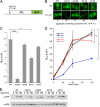
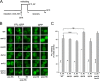
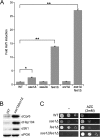
Heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) molecular chaperones play critical roles in protein homeostasis. In the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, cytosolic Hsp70 interacts with up to three types of nucleotide exchange factors (NEFs) homologous to human counterparts: Sse1/Sse2 (Heat shock protein 110 (Hsp110)), Fes1 (HspBP1), and Snl1 (Bag-1). All three NEFs stimulate ADP release; however, it is unclear why multiple distinct families have been maintained throughout eukaryotic evolution. In this study we investigate NEF roles in Hsp70 cell biology using an isogenic combinatorial collection of NEF deletion mutants. Utilizing well characterized model substrates, we find that Sse1 participates in most Hsp70-mediated processes and is of particular importance in protein biogenesis and degradation, whereas Fes1 contributes to a minimal extent. Surprisingly, disaggregation and resolubilization of thermally denatured firefly luciferase occurred independently of NEF activity. Simultaneous deletion of SSE1 and FES1 resulted in constitutive activation of heat shock protein expression mediated by the transcription factor Hsf1, suggesting that these two factors are important for modulating stress response. Fes1 was found to interact in vivo preferentially with the Ssa family of cytosolic Hsp70 and not the co-translational Ssb homolog, consistent with the lack of cold sensitivity and protein biogenesis phenotypes for fes1Δ cells. No significant consequence could be attributed to deletion of the minor Hsp110 SSE2 or the Bag homolog SNL1. Together, these lines of investigation provide a comparative analysis of NEF function in yeast that implies Hsp110 is the principal NEF for cytosolic Hsp70, making it an ideal candidate for therapeutic intervention in human protein folding disorders.
Keywords: Hsp70; Molecular Chaperone; Nucleotide Exchange Factor; Protein Degradation; Protein Folding; Protein Homeostasis; Protein Misfolding; Protein Stability; Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Yeast.
Figures




References
-
- Hartl F. U., Bracher A., Hayer-Hartl M. (2011) Molecular chaperones in protein folding and proteostasis. Nature 475, 324–332 - PubMed
-
- Soto C. (2003) Unfolding the role of protein misfolding in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 4, 49–60 - PubMed
-
- Mayer M. P. (2013) Hsp70 chaperone dynamics and molecular mechanism. Trends Biochem. Sci. 38, 507–514 - PubMed
-
- Vogel M., Bukau B., Mayer M. P. (2006) Allosteric regulation of Hsp70 chaperones by a proline switch. Mol. Cell 21, 359–367 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

