The relationship between mean platelet volume and thrombosis recurrence in patients diagnosed with antiphospholipid syndrome
- PMID: 24671503
- PMCID: PMC4209097
- DOI: 10.1007/s00296-014-2996-0
The relationship between mean platelet volume and thrombosis recurrence in patients diagnosed with antiphospholipid syndrome
Abstract
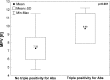
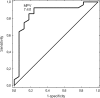
Increased mean platelet volume (MPV) is associated with platelet reactivity and is a predictor of cardiovascular risk and unprovoked venous thromboembolism. The aim of our study was to evaluate MPV in patients with confirmed antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) and to identify the correlation between the value of MPV and the recurrence of thrombosis. The studied group consists of 247 patients with a history of thrombosis and/or pregnancy loss (median age 38, range 18-66 years) classified as APS group (n = 70) or APS negative patients (n = 177) according to the updated Sapporo criteria. The control group consisted of 98 healthy subjects. MPV was significantly higher in the group of patients with clinically and laboratory confirmed APS (median 7.85, range 4.73-12.2 fl) in comparison with the controls. It was also higher than in APS negative patients (7.61, range 5.21-12.3 fl). APS patients with triple positivity for antiphospholipid antibodies with respect to Miyakis classification categories had higher MPV values than other APS patients (9.69 ± 1.85 vs. 7.29 ± 1.3 fl, p = 0.001). Recurrent thrombotic episodes were observed in 83 patients, but among the triple positive high-risk patients with APS in 80 % cases (p = 0.0046). In receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, the value of MPV level for thrombosis recurrence prediction in the APS group with sensitivity of 86 % and specificity of 82 % was 7.4 fl. In the multivariate logistic regression model, MPV above 7.4 fl (OR 3.65; 95 % CI 1.38-9.64, p = 0.009) significantly predicts thrombosis recurrence. Our results identify the value of MPV as a prognostic factor of thrombosis recurrence in patients with APS.
Figures
References
-
- Kahn SR, Lim W, Dunn AS, Cushman M, Dentali F, Akl EA, et al. Prevention of VTE in nonsurgical patients: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2 Suppl):e195S–e226S. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous