Optimal Allocation of Gold Standard Testing under Constrained Availability: Application to Assessment of HIV Treatment Failure
- PMID: 24672142
- PMCID: PMC3963362
- DOI: 10.1080/01621459.2013.810149
Optimal Allocation of Gold Standard Testing under Constrained Availability: Application to Assessment of HIV Treatment Failure
Abstract
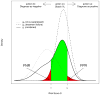
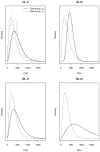
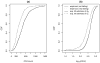
The World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines for monitoring the effectiveness of HIV treatment in resource-limited settings (RLS) are mostly based on clinical and immunological markers (e.g., CD4 cell counts). Recent research indicates that the guidelines are inadequate and can result in high error rates. Viral load (VL) is considered the "gold standard", yet its widespread use is limited by cost and infrastructure. In this paper, we propose a diagnostic algorithm that uses information from routinely-collected clinical and immunological markers to guide a selective use of VL testing for diagnosing HIV treatment failure, under the assumption that VL testing is available only at a certain portion of patient visits. Our algorithm identifies the patient sub-population, such that the use of limited VL testing on them minimizes a pre-defined risk (e.g., misdiagnosis error rate). Diagnostic properties of our proposal algorithm are assessed by simulations. For illustration, data from the Miriam Hospital Immunology Clinic (RI, USA) are analyzed.
Keywords: Antiretroviral failure; HIV/AIDS; ROC; constrained optimization; resource limited; tripartite classification.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson AM, Bartlett JA. Changing antiretroviral therapy in the setting of virologic relapse: review of the current literature. Current HIV/AIDS Reports. 2006;3:79–85. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JA. Separate sample logistic discrimination. Biometrika. 1972;59:19–35.
-
- Anderson JA. Multivariate Logistic Compounds. Biometrika. 1979;66:17–26.
-
- Bagchi S, Kempf M, Westfall A, Maherya A, Willig J, Saag M. Can routine clinical markers be used longitudinally to monitor antiretroviral therapy success in resourcelimited settings? Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2007;44:135–138. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
