A single centre experience of first "one hundred laparoscopic liver resections"
- PMID: 24672143
- PMCID: PMC3942341
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/930953
A single centre experience of first "one hundred laparoscopic liver resections"
Abstract
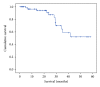
Background. Laparoscopic liver resection (LLR) has emerged as an alternative procedure to open liver resection in selected patients. The purpose of this study was to describe our initial experience of 100 patients undergoing LLR. Methods. We analysed a prospectively maintained hepatobiliary database of 100 patients who underwent LLR between August 2007 and August 2012. Clinicopathological data were reviewed to evaluate surgical outcomes following LLR. Results. The median age was 64 and median BMI 27. Patients had a liver resection for either malignant lesions (n = 74) or benign lesions (n = 26). Commonly performed procedures were segmentectomy/metastectomy (n = 55), left lateral sectionectomy (LLS) (n = 26), or major hepatectomy (n = 19). Complete LLR was performed in 84 patients, 9 were converted to open and 7 hand-assisted. The most common indications were CRLM (n = 62), followed by hepatic adenoma (n = 9) or hepatocellular carcinoma (n = 7). The median operating time was 240 minutes and median blood loss was 250 mL. Major postoperative complications occurred in 9 patients. The median length of stay (LOS) was 5 days. One patient died within 30 days of liver resection. Conclusions. LLR is a safe and oncologically feasible procedure with comparable short-term perioperative outcomes to the open approach. However, further studies are necessary to determine long-term oncological outcomes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Laparoscopic Liver Resection for Tumors in the Left Lateral Liver Section.JSLS. 2016 Jan-Mar;20(1):e2015.00112. doi: 10.4293/JSLS.2015.00112. JSLS. 2016. PMID: 26877627 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic liver resection-understanding its role in current practice: the Henri Mondor Hospital experience.Ann Surg. 2009 Jul;250(1):103-11. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181ad6660. Ann Surg. 2009. PMID: 19561476
-
Laparoscopic liver resection for posterosuperior and anterolateral lesions-a comparison experience in an Asian centre.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2015 Dec;4(6):379-90. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2304-3881.2015.06.06. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26734622 Free PMC article.
-
World review of laparoscopic liver resection-2,804 patients.Ann Surg. 2009 Nov;250(5):831-41. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181b0c4df. Ann Surg. 2009. PMID: 19801936 Review.
-
Short and long-term outcomes of laparoscopic compared to open liver resection for colorectal liver metastases.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2016 Aug;5(4):300-10. doi: 10.21037/hbsn.2016.02.01. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27500142 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Early Experience in Starting a Laparoscopic Liver Resection Program in Greece.JSLS. 2017 Jan-Mar;21(1):e2016.00110. doi: 10.4293/JSLS.2016.00110. JSLS. 2017. PMID: 28701858 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical outcome of laparoscopic hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: A matched case-control study with propensity score matching.J Minim Access Surg. 2018 Oct-Dec;14(4):277-284. doi: 10.4103/jmas.JMAS_116_17. J Minim Access Surg. 2018. PMID: 29226881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gagner M, Rheault M, Dubuc J. Laparoscopic partial hepatectomy for liver tumour. Surgical Endoscopy. 1992;6:p. 99.
-
- Gagner M, Rogula T, Selzer D. Laparoscopic liver resection: benefits and controversies. Surgical Clinics of North America. 2004;84(2):451–462. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen KT, Gamblin TC, Geller DA. World review of laparoscopic liver resection-2804 patients. Annals of Surgery. 2009;250(5):831–841. - PubMed
-
- Buell JF, Cherqui D, Geller DA, et al. The international position on laparoscopic liver surgery: The Louisville Statement, 2008. Annals of Surgery. 2009;250(5):825–830. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources