Study of positional dependence of dose to bladder, pelvic wall and rectal points in High-Dose-Rate Brachytherapy in cervical cancer patients
- PMID: 24672152
- PMCID: PMC3958997
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-6203.121195
Study of positional dependence of dose to bladder, pelvic wall and rectal points in High-Dose-Rate Brachytherapy in cervical cancer patients
Abstract
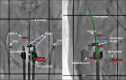
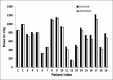
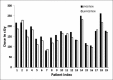
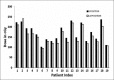
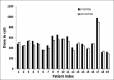
The objective of the study is to examine the variation in doses to, Bladder, pelvic wall and Rectal Points when a patient is simulated in Supine (S Position) and Lithotomy M shaped positions (LM Position), respectively as part of Intracavitary Brachytherapy in Cervical Cancer patients. Patients (n = 19) were simulated and orthogonal images were taken in S Position and LM Positions on a physical simulator. Digital orthogonal X-ray images were transferred to Brachyvision Treatment Planning System via Dicom to generate treatment plans. Radio opaque dye of 7 ml was injected into the Foley bulb for identification and digitization of International Commission on Radiological Units and Measurements (ICRU) Bladder point. Pelvic side wall points were marked in accordance with ICRU 38 recommendations. A Rectal tube containing dummy source marker wire was used to identify Rectal Point. Students't-test was used to analyze the results. Doses in LM Position were lower and statistically significant when compared to S Position for ICRU Bladder Point, pelvic walls and Rectal Point. It was observed that movement of applicator could be the reason for the variations in doses between the two positions. Bladder, pelvic wall and rectal points systematically registered lower doses in LM Position as compared to S Position.
Keywords: Bladder; lithotomy; rectum; supine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparison between CT-based volumetric calculations and ICRU reference-point estimates of radiation doses delivered to bladder and rectum during intracavitary radiotherapy for cervical cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005 May 1;62(1):131-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.09.059. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005. PMID: 15850913
-
Point vs. volumetric bladder and rectal doses in combined intracavitary-interstitial high-dose-rate brachytherapy: correlation and comparison with published Vienna applicator data.Brachytherapy. 2008 Oct-Dec;7(4):336-42. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2008.05.005. Epub 2008 Sep 7. Brachytherapy. 2008. PMID: 18782683
-
Dosimetric evaluation of rectum and bladder using image-based CT planning and orthogonal radiographs with ICRU 38 recommendations in intracavitary brachytherapy.J Med Phys. 2008 Jan;33(1):3-8. doi: 10.4103/0971-6203.39417. J Med Phys. 2008. PMID: 20041045 Free PMC article.
-
CT based 3-dimensional treatment planning of intracavitary brachytherapy for cancer of the cervix: comparison between dose-volume histograms and ICRU point doses to the rectum and bladder.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(13):5259-64. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.13.5259. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 25040985
-
Non isocentric film-based intracavitary brachytherapy planning in cervical cancer: a retrospective dosimetric analysis with CT planning.J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2012 Sep;4(3):129-34. doi: 10.5114/jcb.2012.30678. Epub 2012 Sep 29. J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2012. PMID: 23346141 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Interfraction Variation and Dosimetric Changes in Patients With Cervical Cancer Treated With Intracavitary Brachytherapy.J Glob Oncol. 2018 Sep;4:1-7. doi: 10.1200/JGO.2016.008557. Epub 2017 Jul 6. J Glob Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30241214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Bray F, Pisani P, Parkin DM. IARC Cancer Base No. 5. version 2.0. Lyon: IARC Press; 2004. GLOBOCAN 2002: Cancer Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence Worldwide.
-
- Stitt JA, Fowler JF, Thomadsen BR, Buchler DA, Paliwal BP, Kinsella TJ. High dose rate intracavitary brachytherapy for carcinoma of the cervix: The Madison System: I. Clinical and radiobiological considerations. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992;24:335–48. - PubMed
-
- Brenner DJ, Hall EJ. Fractionated high dose rate versus low dose rate regimens for Intracavitary brachytherapy of the cervix. Br J Radiol. 1991;64:133–41. - PubMed
-
- Eifel PJ. High-dose-rate brachytherapy for carcinoma of the cervix: High tech or high risk? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992;24:383–6. - PubMed
-
- Dale RG. The application of the linear-quadratic dose-effect equation to fractionated and protracted radiotherapy. Br J Radiol. 1985;58:515–28. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

