Frailty syndrome: an overview
- PMID: 24672230
- PMCID: PMC3964027
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S45300
Frailty syndrome: an overview
Abstract
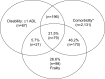
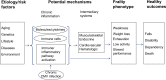
Frailty is a common and important geriatric syndrome characterized by age-associated declines in physiologic reserve and function across multiorgan systems, leading to increased vulnerability for adverse health outcomes. Two major frailty models have been described in the literature. The frailty phenotype defines frailty as a distinct clinical syndrome meeting three or more of five phenotypic criteria: weakness, slowness, low level of physical activity, self-reported exhaustion, and unintentional weight loss. The frailty index defines frailty as cumulative deficits identified in a comprehensive geriatric assessment. Significant progress has recently been made in understanding the pathogenesis of frailty. Chronic inflammation is likely a key pathophysiologic process that contributes to the frailty syndrome directly and indirectly through other intermediate physiologic systems, such as the musculoskeletal, endocrine, and hematologic systems. The complex multifactorial etiologies of frailty also include obesity and specific diseases. Major clinical applications include risk assessment and stratification. This can be applied to the elderly population in the community and in a variety of care settings. Frailty may also be useful for risk assessment in surgical patients and those with cardiovascular diseases, cancer, or human immunodeficiency virus infection, as well as for assessment of vaccine effectiveness in older adults. Currently, exercise and comprehensive geriatric interdisciplinary assessment and treatment are key interventions for frailty. As understanding of the biologic basis and complexity of frailty further improves, more effective and targeted interventional strategies and innovative geriatric-care models will likely be developed.
Keywords: IL-6; aging; frailty; inflammation; older adults.
Figures
References
-
- Fried LP, Hadley EC, Walston JD, et al. From bedside to bench: research agenda for frailty. Sci Aging Knowledge Environ. 2005;2005(31):pe24. - PubMed
-
- Walston J, Hadley EC, Ferrucci L, et al. Research agenda for frailty in older adults: toward a better understanding of physiology and etiology: summary from the American Geriatrics Society/National Institute on Aging Research Conference on Frailty in Older Adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54:991–1001. - PubMed
-
- Lipsitz LA. Dynamics of stability: the physiologic basis of functional health and frailty. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2002;57:115–125. - PubMed
-
- Fried LP, Tangen C, Walston J, et al. Frailty in older adults: evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001;56A:M1–M11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

