Efficacy and safety of Curcuma domestica extracts compared with ibuprofen in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a multicenter study
- PMID: 24672232
- PMCID: PMC3964021
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S58535
Efficacy and safety of Curcuma domestica extracts compared with ibuprofen in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a multicenter study
Abstract
Objective: To determine the efficacy and safety of Curcuma domestica extracts in pain reduction and functional improvement.
Methods: 367 primary knee osteoarthritis patients with a pain score of 5 or higher were randomized to receive ibuprofen 1,200 mg/day or C. domestica extracts 1,500 mg/day for 4 weeks. The main outcomes were Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) total, WOMAC pain, WOMAC stiffness, and WOMAC function scores. Adverse events (AEs) were also recorded.
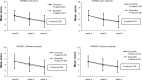
Results: 185 and 182 patients were randomly assigned into C. domestica extracts and ibuprofen groups, respectively. The baseline characteristics were no different between groups. The mean of all WOMAC scores at weeks 0, 2, and 4 showed significant improvement when compared with the baseline in both groups. After using the noninferiority test, the mean difference (95% confidence interval) of WOMAC total, WOMAC pain, and WOMAC function scores at week 4 adjusted by values at week 0 of C. domestica extracts were noninferior to those for the ibuprofen group (P=0.010, P=0.018, and P=0.010, respectively), except for the WOMAC stiffness subscale, which showed a trend toward significance (P=0.060). The number of patients who developed AEs was no different between groups. However, the number of events of abdominal pain/discomfort was significantly higher in the ibuprofen group than that in the C. domestica extracts group (P=0.046). Most subjects (96%-97%) were satisfied with the treatment, and two-thirds rated themselves as improved in a global assessment.
Conclusion: C. domestica extracts are as effective as ibuprofen for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. The side effect profile was similar but with fewer gastrointestinal AE reports in the C. domestica extracts group.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00792818.
Keywords: Curcuma domestica; curcumin; efficacy; ibuprofen; knee osteoarthritis; safety.
Figures

Comment in
-
Importance of acute renal failure with ibuprofen.Clin Interv Aging. 2014 May 5;9:763. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S64674. eCollection 2014. Clin Interv Aging. 2014. PMID: 24904203 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Author's reply: To PMID 24672232.Clin Interv Aging. 2014;9:764. Clin Interv Aging. 2014. PMID: 24968462 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fransen M, Bridgett L, March L, Hoy D, Penserga E, Brooks P. The epidemiology of osteoarthritis in Asia. Int J Rheum Dis. 2011;14(2):113–121. - PubMed
-
- March LM, Bagga H. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis in Australia. Med J Aust. 2004;180(Suppl 5):S6–S10. - PubMed
-
- Suri P, Morgenroth DC, Hunter DJ. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis and associated comorbidities. PM R. 2012;4(Suppl 5):S10–S19. - PubMed
-
- Du H, Chen SL, Bao CD, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis in Huang-Pu District, Shanghai, China. Rheumatol Int. 2005;25(8):585–590. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

